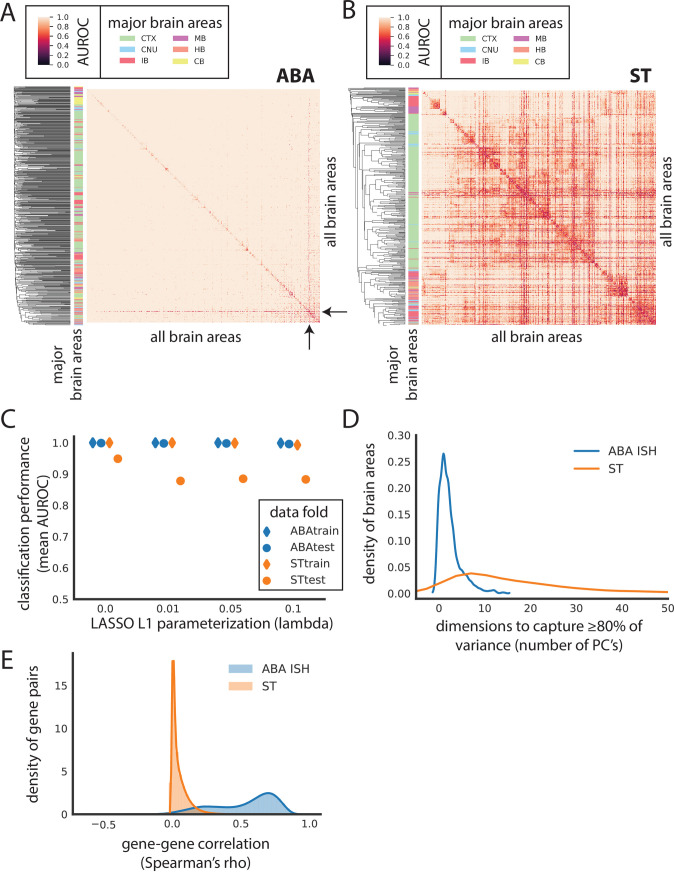
Fig 2. Canonical brain areas are classifiable using gene expression alone in the ABA and ST datasets.
Heat map of AUROC for classifying leaf brain areas from all other leaf brain areas in (A) ABA and (B) ST using LASSO (lambda = 0.1). Dendrograms on the far left side represent clustering of leaf brain areas based on the inverse of AUROC; areas with an AUROC near 0.5 get clustered together, while areas with an AUROC near 1 are further apart. Color bar on the left represents the major brain structure that the leaf brain area is grouped under. These areas include CTX, MB, CB, CNU, HB, and IB. (C) Average AUROC (y-axis) of classifying all brain areas from all other brain areas using LASSO across various values of lambda (x-axis): 0, 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 for ABA train (blue diamond), ABA test (blue dot), ST train (orange diamond), and ST test (orange dot). (D) Number of principal components to capture at least 80% of variance of genes in each of the leaf brain areas after applying PCA to ABA (blue) and ST (orange). ABA brain areas that are larger than ST are randomly down-sampled to have the same number of samples as ST prior to applying PCA. (E) Gene–gene correlations calculated as Spearman’s rho between all pairwise genes across the whole dataset for both the ABA (blue) and ST (orange) independently. ABA, Allen Brain Atlas; AUROC, area under the receiver operating curve; CB, cerebellum; CNU, striatum and pallidum; CTX, cortex; HB, hindbrain; IB, thalamus and hypothalamus; ISH, in situ hybridization; LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MB, midbrain; PCA, principal component analysis; ST, spatial transcriptomics.