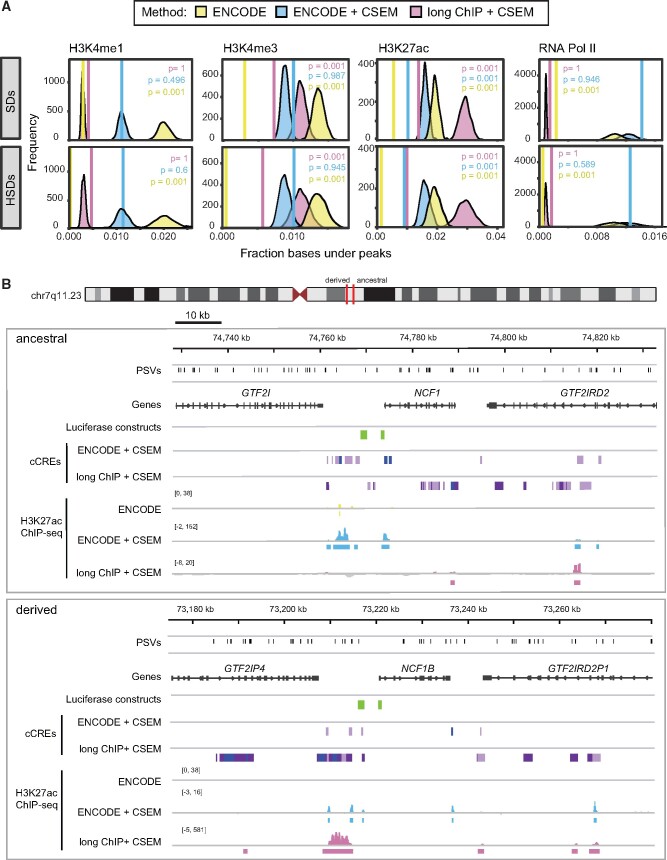
Fig. 3.
Depletion and recovery of ChIP peaks in SDs. (A) The fraction of bases covered by peaks (solid vertical line) was computed in SDs (top) and HSDs (SDs >98% sequence identity, bottom) for three ChIP-seq peak discovery approaches: publicly available ENCODE peaks (yellow), peaks from multimapping and CSEM allocation of ENCODE raw data (blue), and peaks from multimapping and CSEM allocation of large-insert ChIP-sequencing (“long ChIP”) data from this publication (magenta). SD coordinates were permuted 1000 times within the human reference (GRCh38), and an expected distribution of the fraction of bases covered was generated. Empirical one-sided P-values for depletion are indicated in each graph. (B) Chromatin landscape at the chromosome 7q11.23 HSD locus. The ancestral locus (top) and one of its derived loci (bottom) are shown with PSVs (black), genes (gray), and luciferase-tested regions (green). cCREs were identified with an 8-state ChromHMM model of GM12878 H3K4me3, H3K4me1, and H3K27ac data from multimapping reanalysis of ENCODE and long ChIP data after CSEM allocation (enhancer states in light and dark purple and promoter states in blue). H3K27ac ChIP-seq data (signal and peak calls) are also shown in yellow, blue, and magenta for published ENCODE, reanalyzed ENCODE + CSEM, and long ChIP + CSEM, respectively.