Fig. 1.
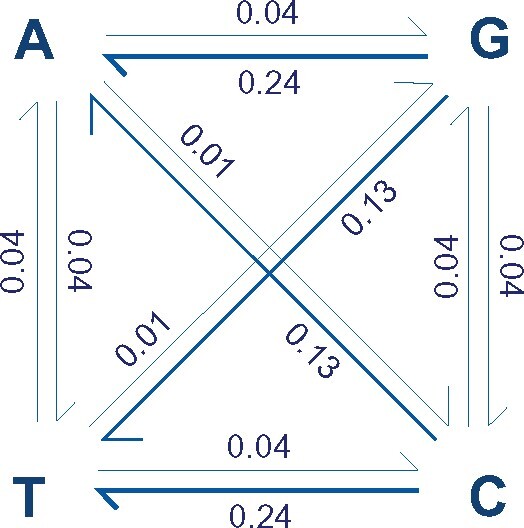
Nucleotide substitution matrix. For each SNP, variants were classified as ancestral (the nucleotide segregating at higher frequency) or derived (the nucleotide segregating at lower frequency). Derived variants were considered mutations from the ancestral allele, and the proportion of all mutations from one nucleotide to each other nucleotide was estimated. Values are proportions of mutations that belong to each category. For example, 1% of all mutations are A to C transversions.
