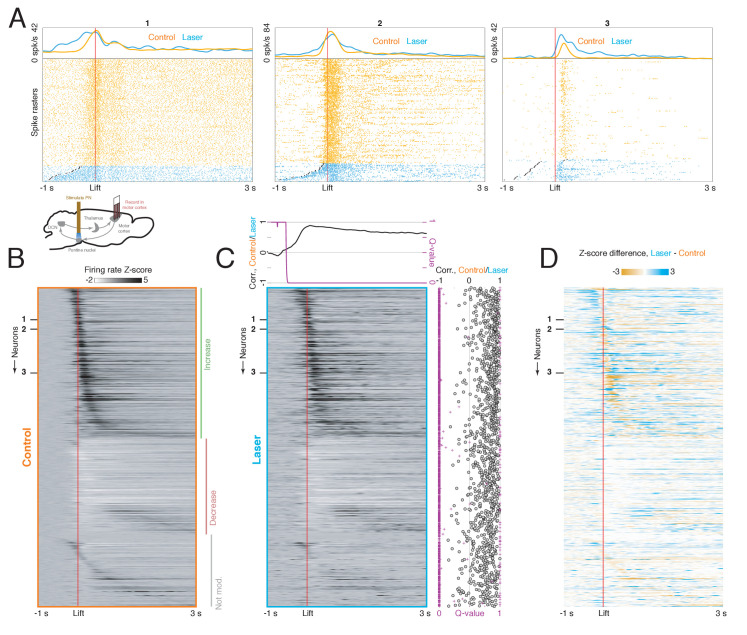
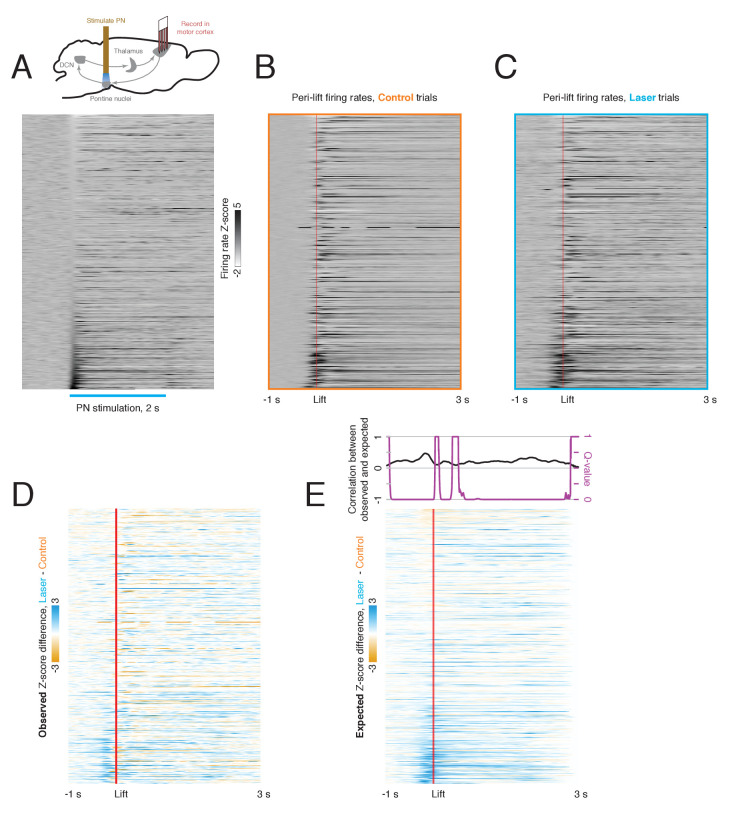
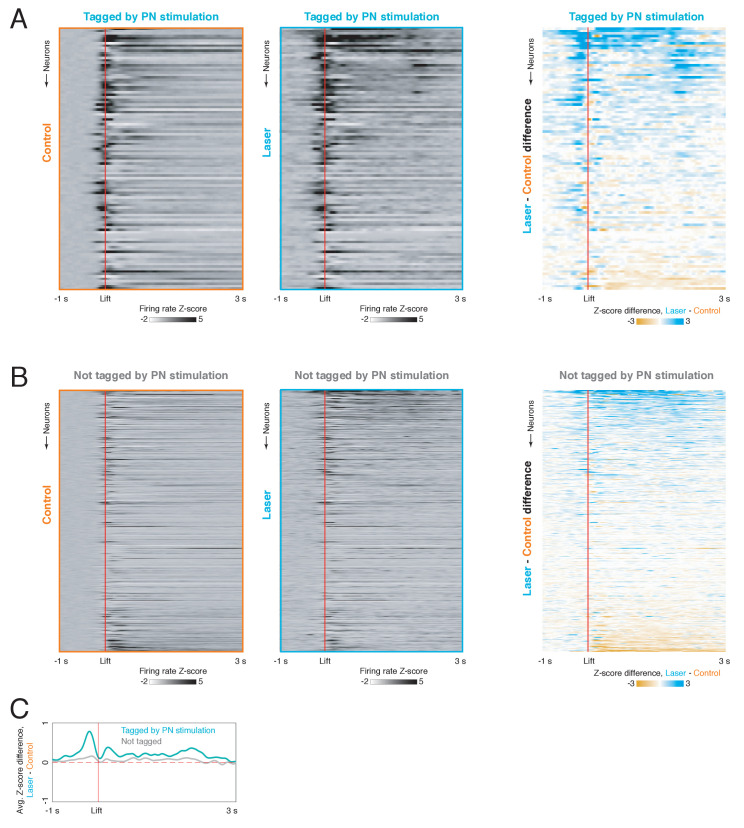
Figure 7. Effect of pontine nuclei (PN) stimulation on neural activity in motor cortex during reaching.
(A) Lower inset: experimental schematic. Animals performed the reaching task as neural activity in motor cortex was recorded. On some trials, PN neurons were activated with a 40 Hz, 2 s laser stimulus. Top panels: lift-aligned spike times and average firing rates on control and laser trials for three motor cortex neurons. Black dots indicate the laser onset. (B) Heatmap displaying lift-aligned average firing rate z-scores on control trials for all motor cortex neurons (n = 1157 neurons, n = 10 mice). (C) Heatmap displaying lift-aligned average firing rate z-scores for laser trials. Upper inset: the black line shows the rank correlation (Spearman’s ρ) between firing rates of the 1157 neurons on control and laser trials at each time point. The magenta inset shows the q-value against the null hypothesis that the correlation is zero. Right inset: black circles show the rank correlation (Spearman’s ρ) between the control and laser firing rates over time for each neuron. Magenta crosses show the q-value against the null hypothesis that the correlation of control and laser values over time is zero. (D) Difference between lift-aligned z-scores for control and laser trials. Orange regions indicate neurons and time points in which the firing rate is higher on control trials, and blue regions indicate points in which the firing rate is higher on laser trials.