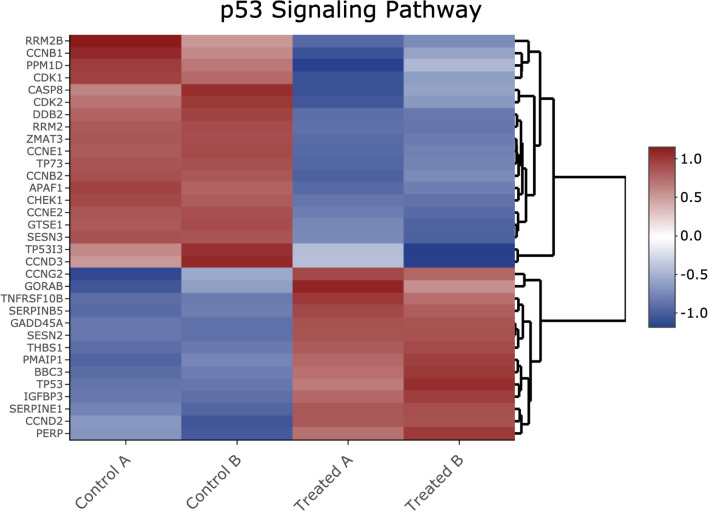
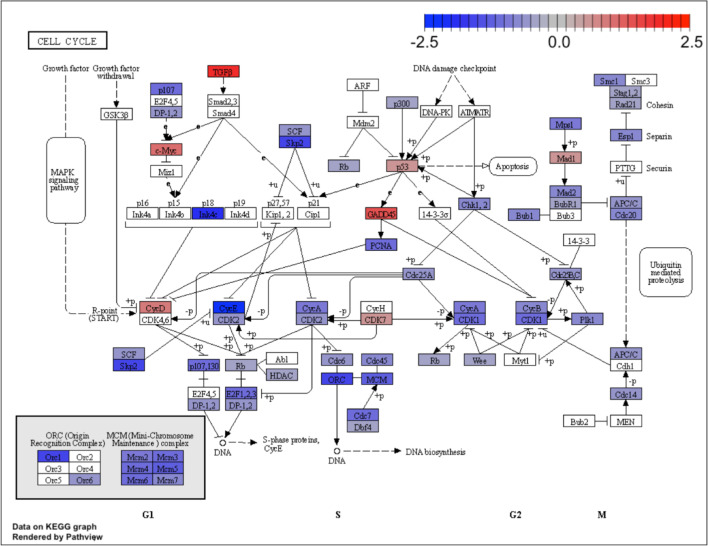
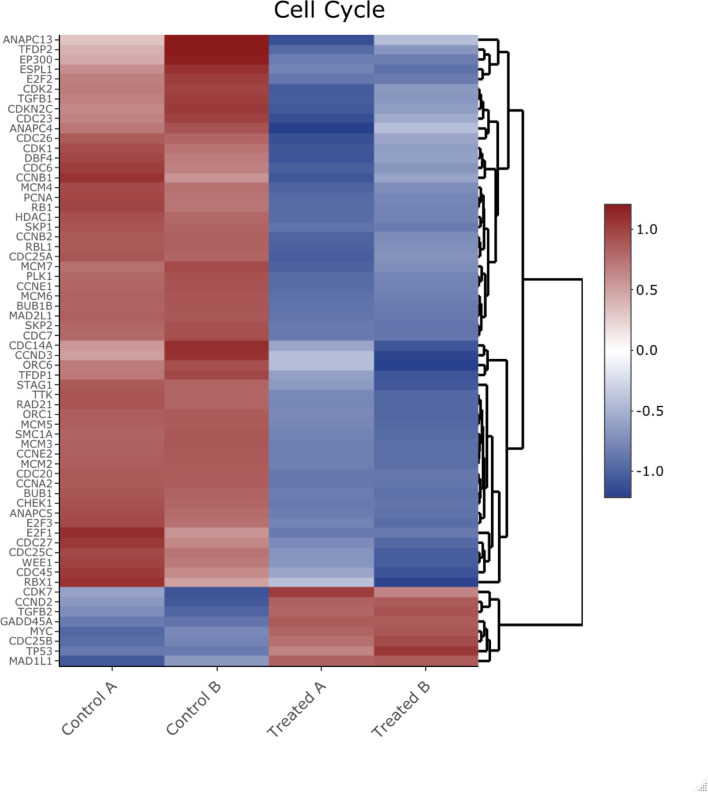
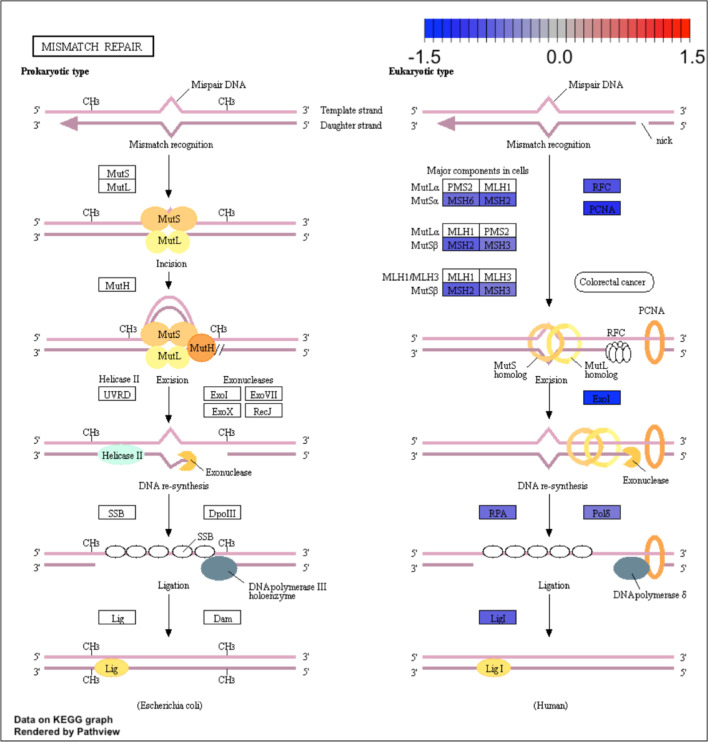
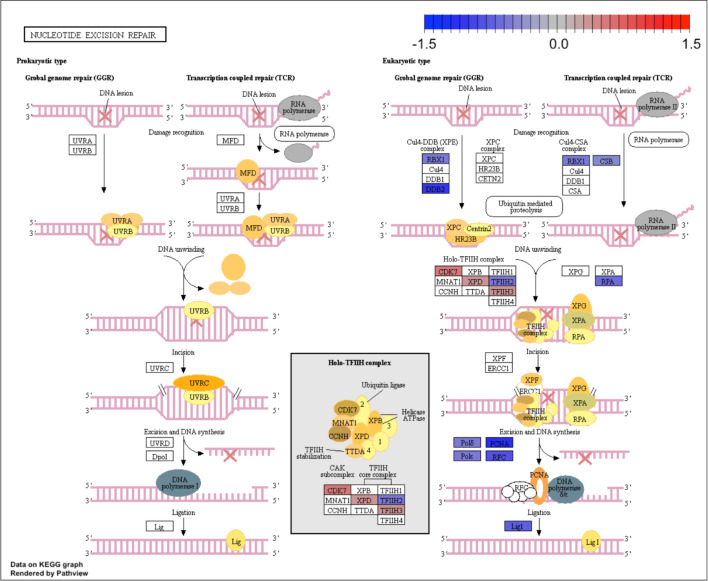
Figure 2. Transcriptomic pathway analysis of analog #4 reveals differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in tumor cells with mutant p53.
SW480 cells were treated with analog #4 for 12 hr. Three-way Venn diagram of all genes tested that met the low expression cutoff (pink), DEGs with an FDR<0.05 (purple), and the known p53 target gene set (A). Heatmap of DEGs that overlapped with the known p53 target gene set (B). Predictive transcription factor analysis according to direct binding motif was performed for all the DEGs (total genes 3362) (C). Four-way Venn diagram of DEGs with an FDR<0.05 (purple), and the known p53 target gene set from Table S3 of Fischer, 2017 (green), ATF4 gene set (yellow), and E2F gene set (pink) (D).