Figure 5. Lung epithelial cell expression and airway release of RELM-α is IL-13 dependent.
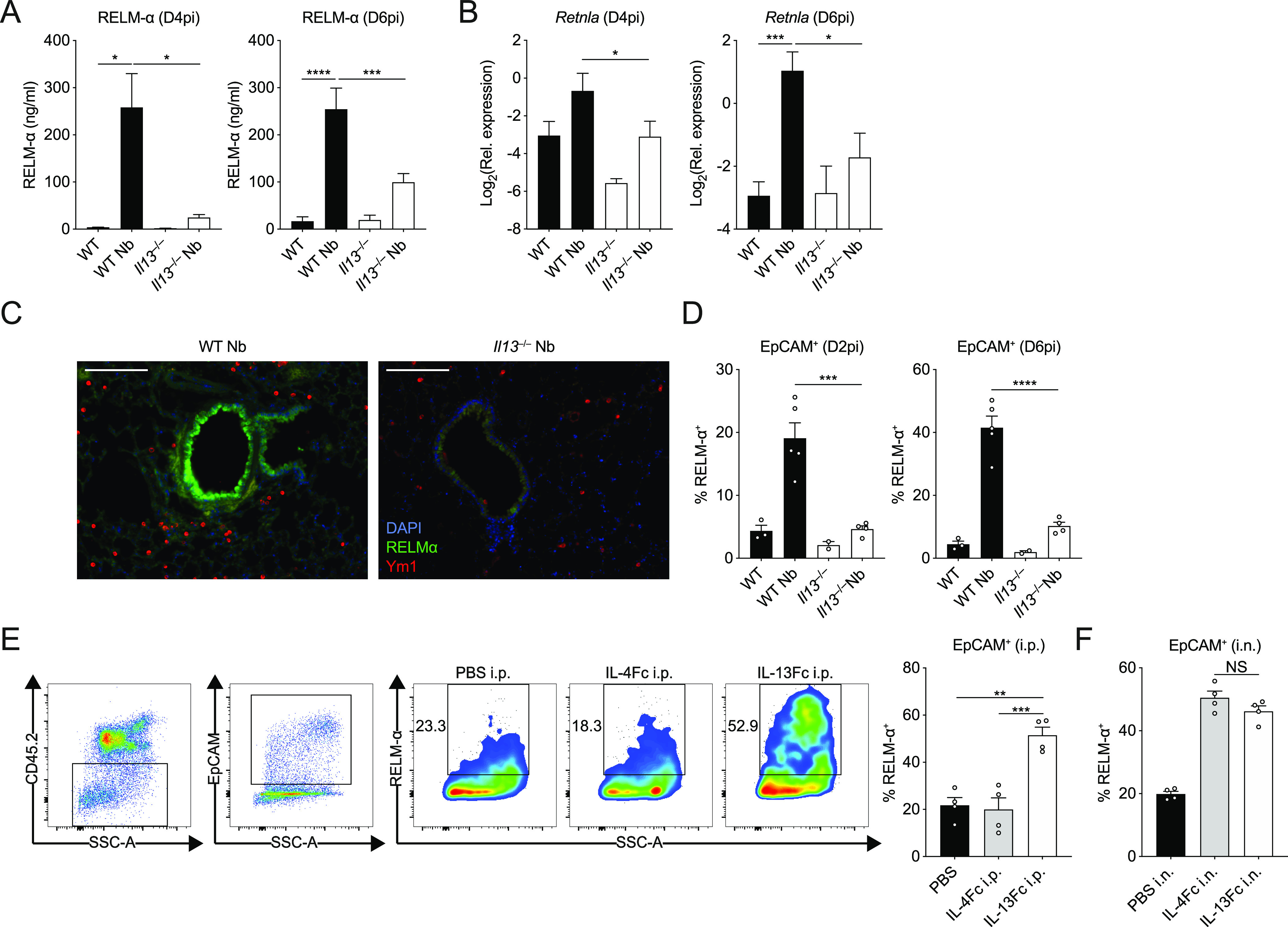
WT and Il13−/− mice were infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb). (A) On D4 and D6pi RELM-α protein levels in the BAL fluid were measured by ELISA. (B) D4 and D6pi whole lung Retnla mRNA was measured by quantitative real-time PCR (data normalised against housekeeping gene Rpl13a). (C) Lung RELM-α (green) and Ym1 (red) were imaged by immunofluorescence microscopy (scale bar = 100 µm). (D) On D2 and D6pi, CD45−EpCAM+ lung epithelial cells were analysed and quantified by flow cytometry to measure intracellular RELM-α. (E, F) WT mice were injected with either PBS, IL-4Fc, or IL-13Fc i.p. or (F) i.n. and 18 h later, CD45−EpCAM+ lung epithelial cell RELM-α expression was measured by flow cytometry. (A, B) Data (mean ± SEM) in (A, B) were pooled from three individual experiments with three to five mice per group (per experiment). (C, D, E, F) Data (mean ± SEM) in (C, D, E, F) were representative of two individual experiments with two to five mice per group (per experiment). NS: not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey–Kramer post hoc test).
