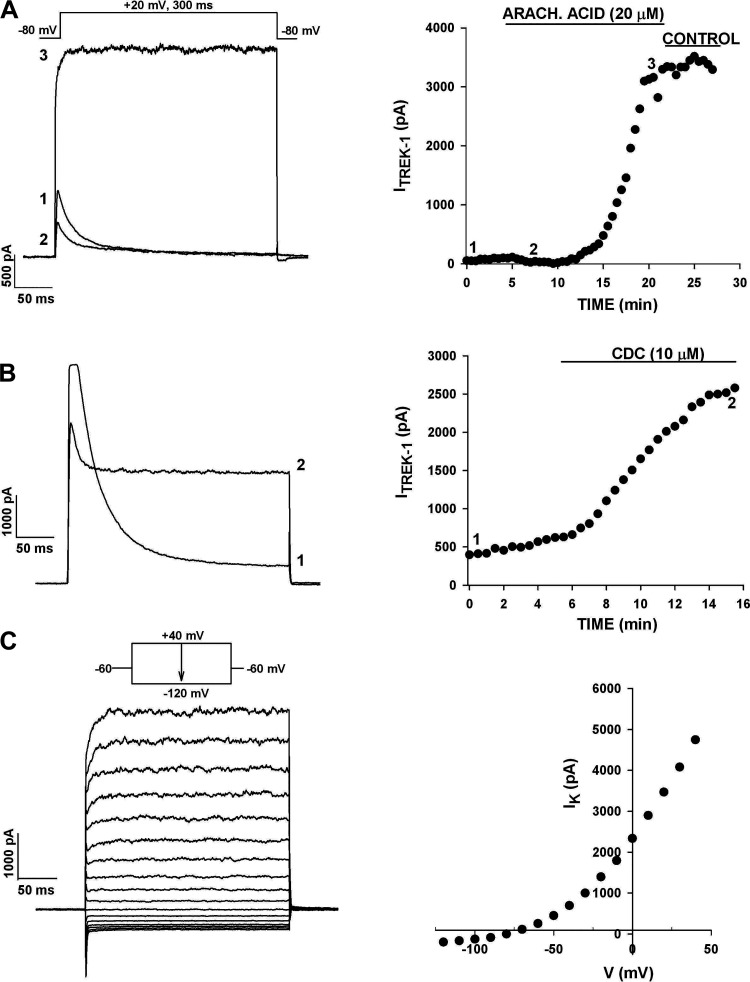
Figure 4.
Arachidonic acid (AA) and cinnamyl 1–3,4-dihydroxy-α-cyano-cinnamate (CDC) activate the leak-type K+ current in human AZG cells. Whole cell recordings of K+ currents were made from human AZG cells that had been in culture for up to 48 h. After recording K+ currents in standard saline, cells were superfused with AA or CDC. A: effect of AA. K+ currents were activated by voltage steps to +20 mV applied at 30 s intervals from a holding potential of −80 mV. After 5 min, the cell was superfused with 20 µM AA. Numbers on current traces correspond to those in the plot of current amplitudes against time at right. B: effect of CDC. K+ currents were recorded, as described in A. After 6 min, the cell was superfused with 10 µM CDC. Numbers on current traces correspond to those on plot of current amplitudes at right. C: CDC and I-V. Whole cell K+ currents were recorded from the same cell as in B by applying voltage steps of 300-ms duration in 10 mV increments to test potentials between +40 and −110 mV from a holding potential of −60 mV. Current amplitudes measured at the midpoint of the traces at left are plotted against test potential at right. Number of independent experiments: n = 6 (A); n = 6 (B and C).