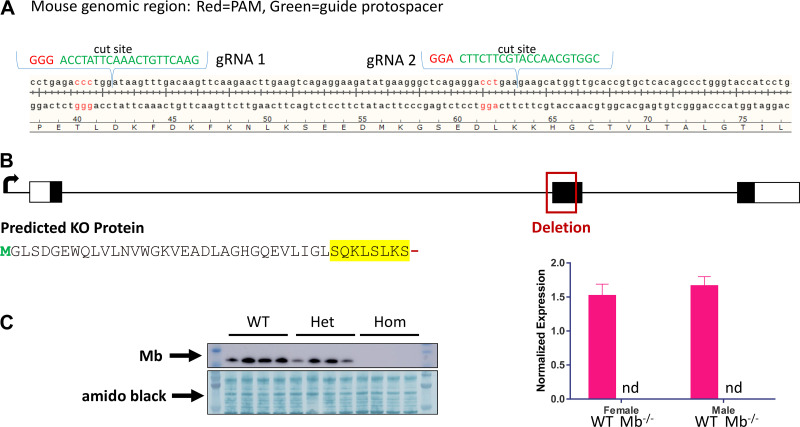
Figure 1.
CRISPR-Cas9 strategy to generate myoglobin (Mb) mutations, resulting in a Mb knockout mouse line. A: example CRISPR-Cas9 design for targeting Mb mutations. B: genomic and translational aspects of the Mb knockout line used for metabolic phenotyping studies, illustrating deletion of much of exon 2 leading to a predicted truncation and amino acid sequence change, shown in yellow (see methods). C: confirmation of Mb null in a subset of mice by Western blot (subsample of whole gastrocnemius from 12-wk-old males and females, n = 2 ea per genotype, chow diet). Also shown are results from qPCR demonstrating no detectable Mb mRNA in gastrocnemius samples collected at the end of the metabolic phenotyping study (females, n = 9/genotype; males, n = 10/genotype). For detection of myoglobin expression, a PrimeTime STD qPCR Assay (Integrated DNA Technologies, IDT) was designed using IDT’s Realtime PCR Tool. The assay was designed to cover the mouse genomic region containing the insertion/deletion region of the myoglobin gene using forward primer: 5′- CCTCTGAGCCCTTCATATCTTC-3′; reverse primer: 5′- GAAGTCCTCATCGGTCTGTTT-3′; probe: 5′-/56-FAM/ AAGACTCAC/ZEN/ CCTGAGACCCTGGAT/3IABkFQ/-3′. WT, wild type; Het, heterozygous; Hom, homozygous knockout.