Figure 3.
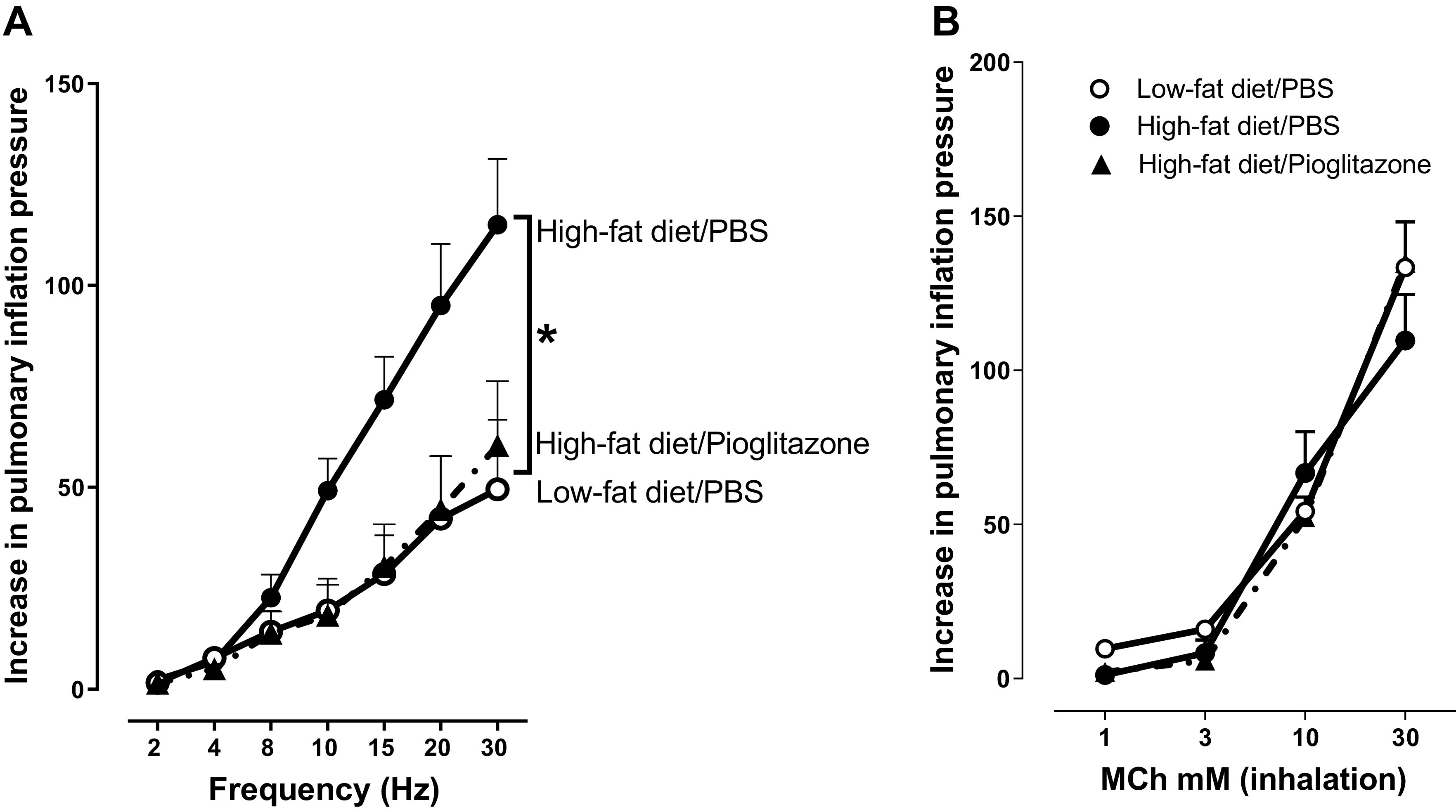
Airway physiology in vagotomized rats. A airway responsiveness was measured by electrically stimulating the vagus nerves with increasing frequency to cause frequency-dependent bronchoconstriction (measured as an increase in pulmonary inflation pressure) in vagotomized, anesthetized rats. B airway smooth muscle function was determined by measuring increased pulmonary inflation pressure in response to increasing concentrations (1–30 mM) of aerosolized methacholine (MCh) delivered in 20 µL saline in vagotomized, anesthetized rats. n = 4–6. *P < 0.05.
