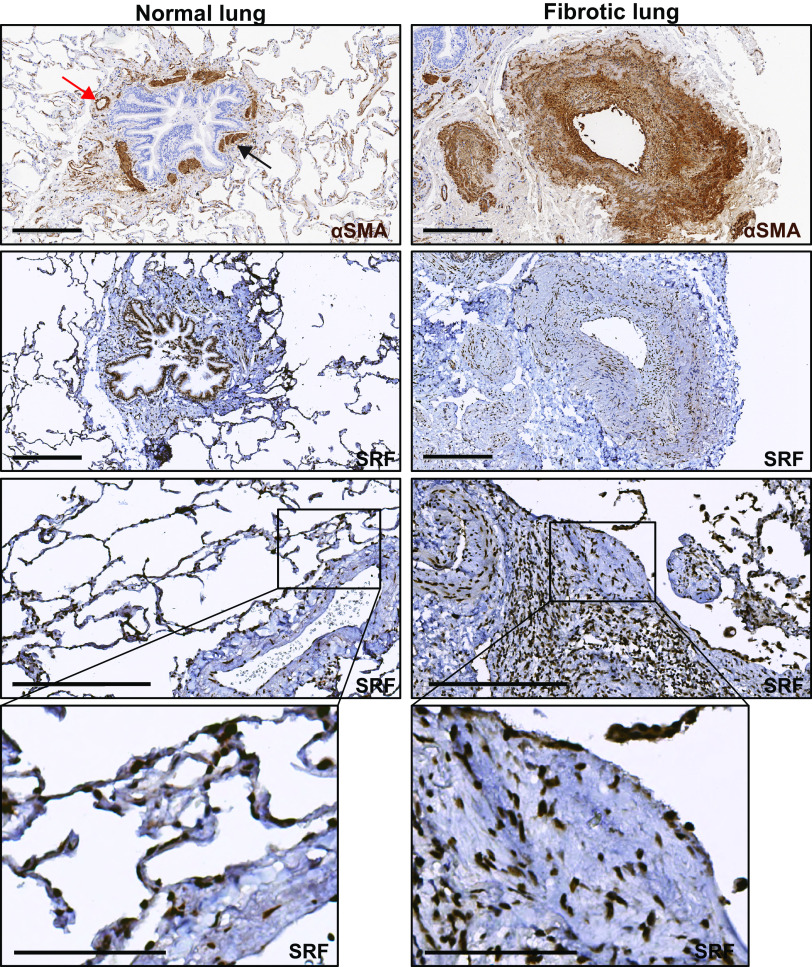
Figure 1.
Serum response factor (SRF) expression is increased in fibrotic regions of human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Immunohistochemical staining of normal and IPF lung samples (n = 3 subjects for each condition) against smooth muscle α actin (αSMA) and SRF. First row: normal (left) and fibrotic (right) lung samples were stained against αSMA. Normal lung (first row, left) shows increased αSMA stain predominantly in the muscularized bands of large airway (black arrow) and vessel (red arrow). SRF staining of normal samples (left column, second through fourth rows) shows localization of SRF staining to the same airway muscle bands (second row), vessel walls, and some nuclei of the alveolar walls (third and fourth rows). Right column shows increased αSMA stain (first row) in the fibrotic interstitium and in the expanded interstitium around a large vessel. SRF staining of fibrotic samples (right column, second through fourth rows) shows localization of increased nuclear SRF staining in the areas of αSMA stain in the fibrotic interstitium and vessel wall. Areas that are morphologically consistent with a fibroblastic focus (third and fourth row) show SRF staining both within and in the surrounding interstitium. Harris hematoxylin counterstain was performed for nuclear labeling in all stains. Scale bar = 300 μm (rows 1–3). Fourth row: digitally zoomed regions of increased expression of SRF in the blood vessel (left, normal) and fibroblastic focus (right, fibrotic). Scale bar = 100 μm (row 4).