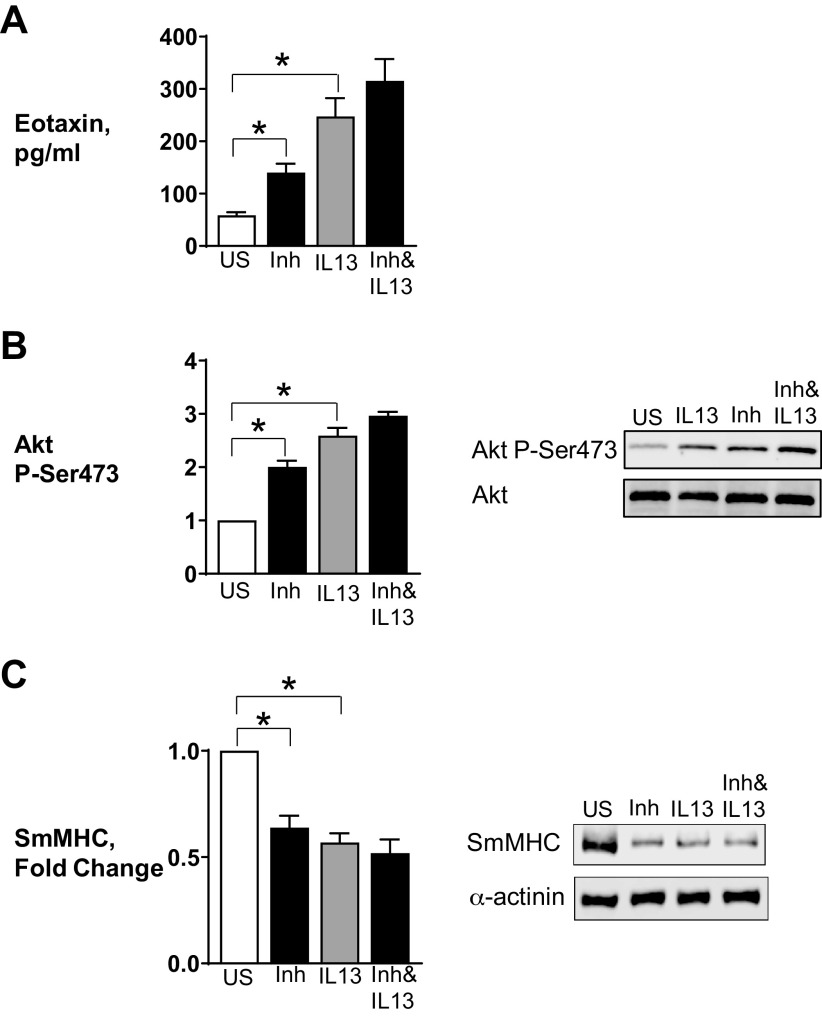
Figure 2.
Inhibition of furin activity promotes inflammatory signaling pathways in airway smooth muscle tissues. Airway smooth muscle tissues were treated with 100 µM Furin Inhibitor II in the presence or absence of 50 ng/mL IL-13 for measurement of Akt phosphorylation, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (SmMHC), or eotaxin secretion. A: eotaxin secretion was significantly increased by Furin Inhibitor II (P = 0.0487) or IL-13 (P = 0.0001) in airway smooth muscle (ASM) tissues (n = 6). Inhibition of furin activity did not significantly increase eotaxin secretion induced by IL-13 (n = 6, P = 0.116). B: treatment of tissues with Furin Inhibitor II or IL-13 results in a significant increase in Akt phosphorylation (n = 8, P = 0.0001). C: expression of SmMHC was significantly inhibited by Furin Inhibitor II or IL-13 (n = 6, P = 0.0001). Furin inhibition did not significantly depress the expression of SmMHC of ASM tissues after IL-13 stimulation (n = 6, P = 0.058). Statistical analysis was performed by using one-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Values are means ± SE. *Significant difference between groups. Inh, Furin Inhibitor II; US, unstimulated.