Figure 6.
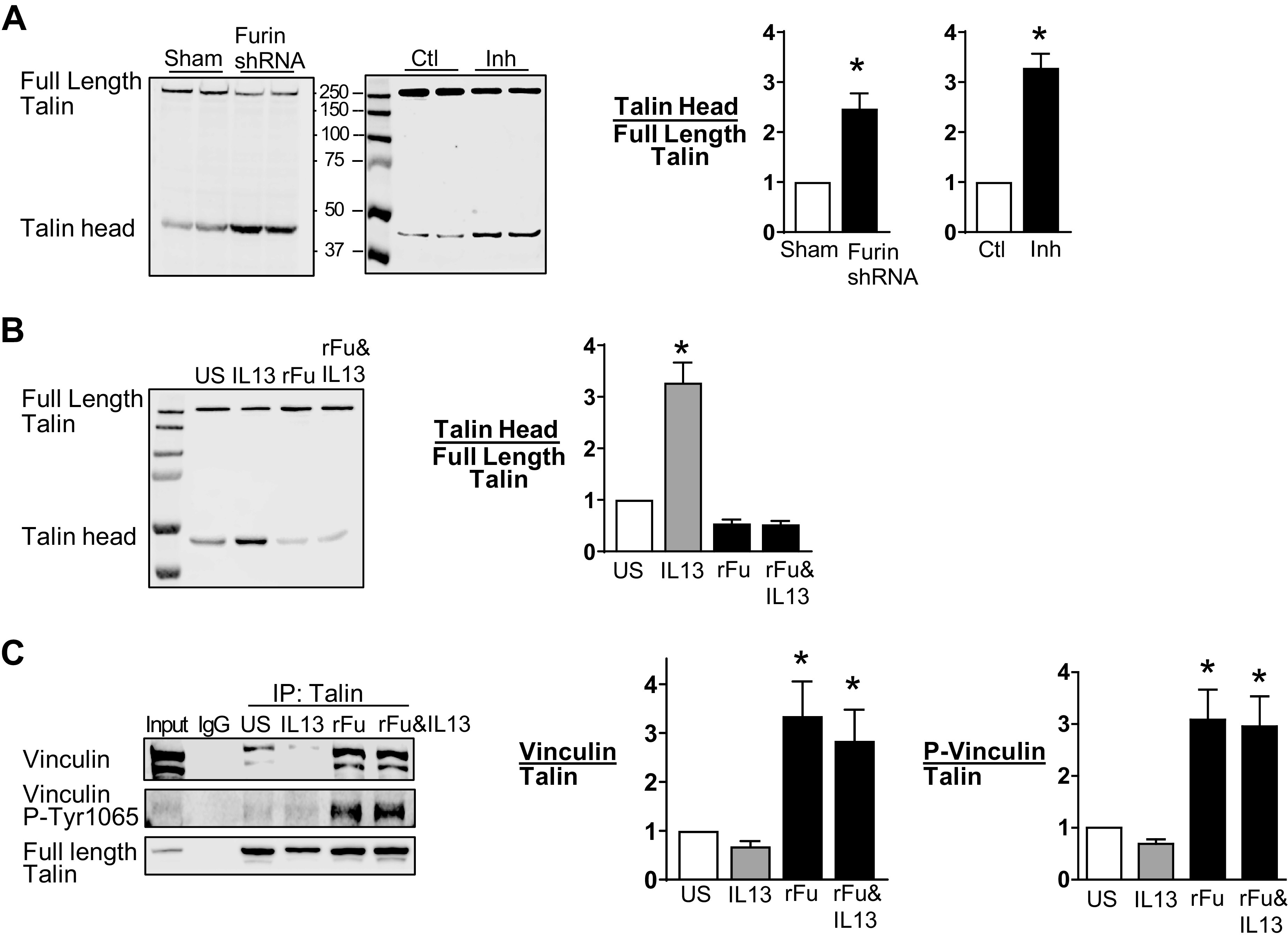
Furin prevents IL-13-induced talin cleavage in airway smooth muscle tissues. A: representative immunoblots from extracts of tissues treated with furin shRNA or sham treated and treated with or without Furin Inhibitor II (Inh). Full-length talin and the talin head domain were analyzed by immunoblot with an N-terminal antibody to talin. Furin depletion significantly increased the ratio of the talin head domain to full-length talin (n = 6, P = 0.005). Furin inhibition also significantly increased the ratio of the talin head domain to full-length talin (n = 15, P = 0.0001). B: representative immunoblot of extracts from tissues treated with or without IL-13 in the presence or absence of recombinant furin (rFurin). IL-13 significantly increased the ratio of the talin head to full-length talin (n = 12, P = 0.0001). rFurin prevented the increase in talin cleavage induced by IL-13 (n = 12, P = 0.2972). C: talin was immunoprecipitated from tissue extracts, and immunocomplexes were blotted for vinculin and Tyr1065 phosphorylated vinculin. Vinculin and phosphorylated vinculin were significantly higher in tissues treated with rFurin or rFurin and IL-13 compared with untreated tissues (vinculin: P = 0.0026 for rFurin, P = 0.0184 for rFurin and IL-13; phosphorylated vinculin: P = 0.0014 for rFurin, P = 0.0026 for rFurin and IL-13) (n = 7). Data were analyzed by using a paired Student’s t test (A) or one-way ANOVA (B and C). All values are means ± SE. *Significant difference between groups. ctl, control; rFu, rFurin; US, unstimulated.
