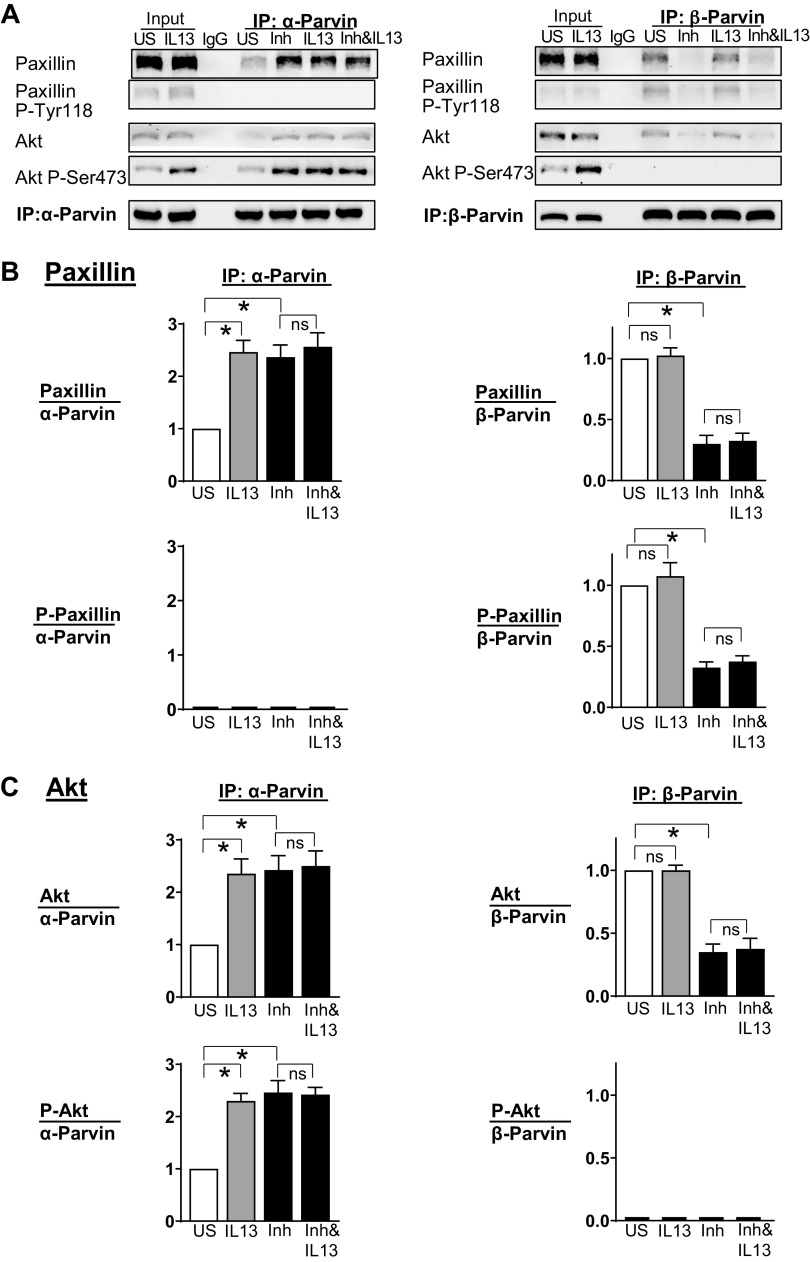
Figure 8.
Furin inhibition promotes the activation of Akt by α-parvin IPP [integrin-linked kinase (ILK), PINCH, parvin] complexes in airway smooth muscle tissues. α-Parvin or β-parvin was immunoprecipitated from extracts of tissues treated with or without IL-13, Furin Inhibitor II, or IL-13 and Furin Inhibitor II. A: α-parvin and β-parvin immunocomplexes were immunoblotted for Akt, pS473-Akt, paxillin, pY118-paxillin, and α-parvin or β-parvin. B: IL-13 and Furin Inhibitor II each stimulates a significant increase in the association of unphosphorylated paxillin with α-parvin IPP complexes (IL-13: n = 5, P = 0.0001; Furin Inhibitor II: n = 5, P = 0.0017). Furin Inhibitor II stimulates a significant decrease in the association of paxillin with β-parvin IPP complexes (n = 4, P = 0.0001). C: IL-13 and Furin Inhibitor II each induces Akt activation by stimulating the association of Akt with α-parvin IPP complexes (IL-13: n = 5, P = 0.0009; Furin Inhibitor II: n = 5, P = 0.0006). Furin Inhibitor II stimulates a significant decrease in the association of Akt with β-parvin IPP complexes (n = 4, P = 0.0001). Statistical analysis was performed by using one-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Values are means ± SE. *Significant difference between groups. Inh, Furin Inhibitor II; ns, no significant difference; US, unstimulated.