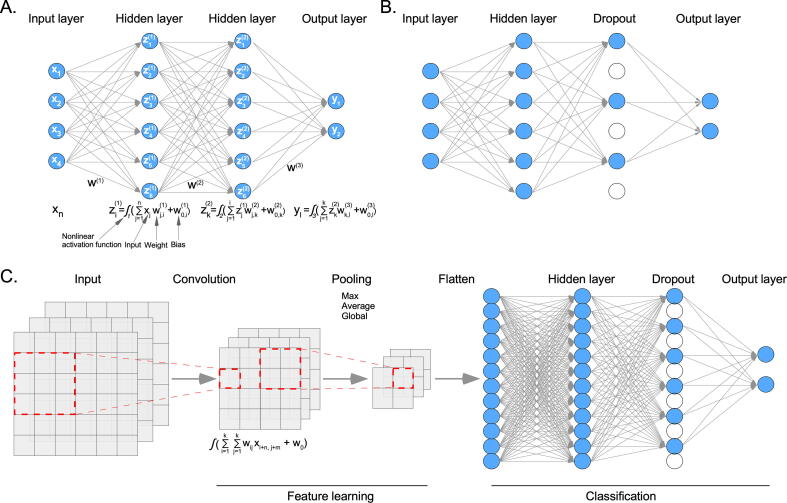
Fig. 6.
Deep learning (DL). (A) In a deep neural network (DNN) model, each node of the input data layer is fully connected to the hidden layer nodes. The first hidden layer takes input data, multiplies it by weight, and adds a bias before applying a nonlinear activation function. The second hidden layer takes the first hidden layer as input and so on until it reaches the output layer. (B) In a dropout layer, some nodes are randomly removed. (C) During the convolution, the dimension of input data is reduced using a certain kernel size (in this example, 3x3) and the activation function. Then, features are pulled for further reduction. Finally, pulled features are flattened and applied to a DNN.