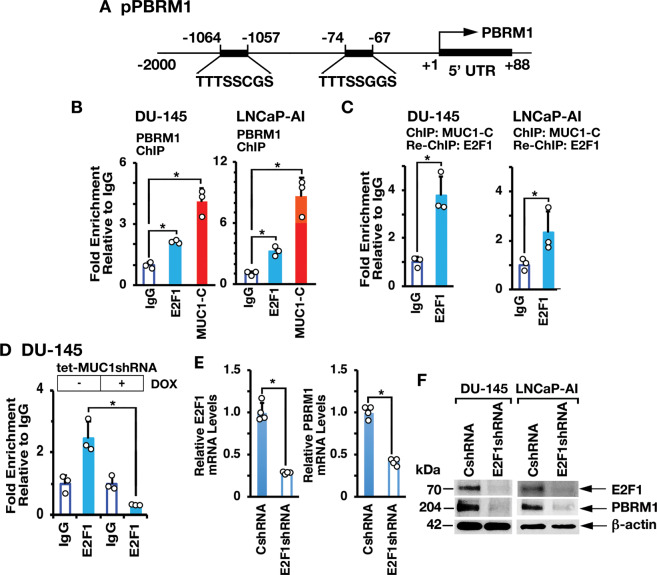
Fig. 2. MUC1-C drives PBRM1 expression by an E2F1-mediated pathway.
A Schema of the PBRM1 promoter region with highlighting of putative E2F binding sites. B Soluble chromatin from DU-145 (left) and LNCaP-AI (right) cells was precipitated with anti-E2F1, anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. C Soluble chromatin from DU-145 (left) and LNCaP-AI (right) cells was precipitated with anti-MUC1-C (ChIP) and then reprecipitated with anti-E2F1 or a control IgG (re-ChIP). D DU-145/tet-MUC1shRNA cells were treated with vehicle or DOX for 7 days. Soluble chromatin was precipitated with anti-E2F1 or a control IgG. The DNA samples were amplified by qPCR with primers for the PBRM1 promoter region. The results (mean ± SD of 3 determinations) are expressed as fold enrichment relative to that obtained with the IgG control (assigned a value of 1). E DU-145/CshRNA and DU-145/E2F1shRNA cells were analyzed for E2F1 and PBRM1 mRNA levels by qRT-PCR. The results (mean ± SD of 4 determinations) are expressed as relative mRNA levels compared to that obtained for CshRNA cells (assigned a value of 1). F Lysates from DU-145/CshRNA and DU-145/E2F1shRNA (left) or LNCaP-AI/CshRNA and LNCaP-AI/E2F1shRNA (right) cells were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins.