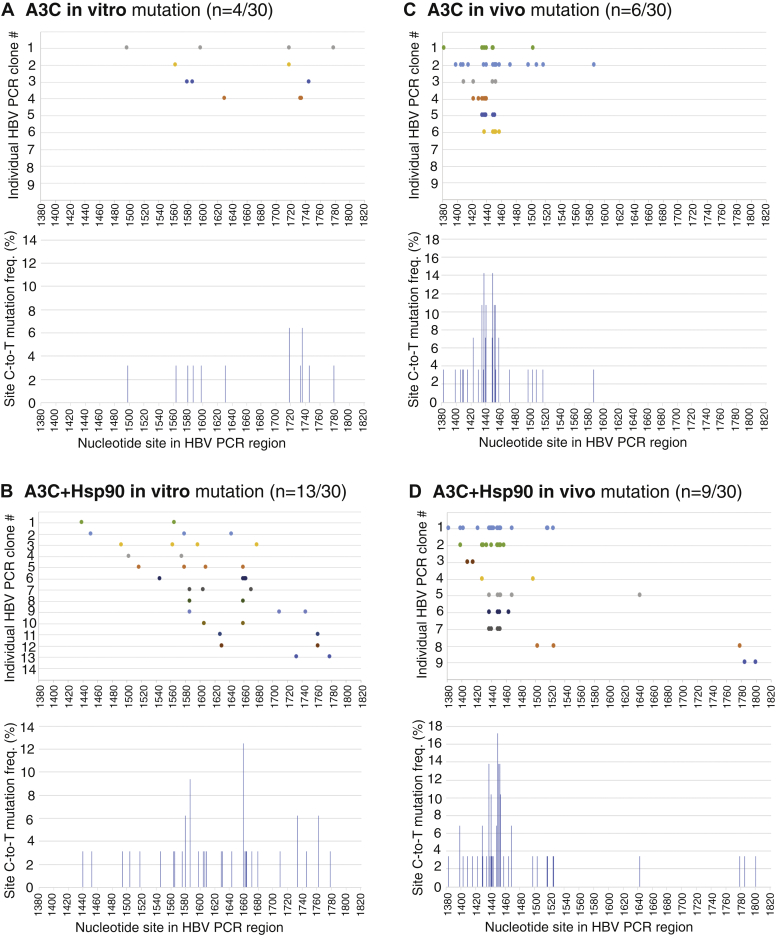
Figure 10.
In vitro and in vivo APOBEC3C mutation comparison. For in vitro mutation, purified A3C with or without Hsp90 was incubated with HBV cDNA fragment (nt 1175–2089) substrate at 30 °C for 3 h. The HBV DNAs were then extracted and amplified by PCR-94 °C followed by 3D-PCR at 88 °C using an inner primer pair to recover the region 1380 to 1820 nt. The resultant 88 °C 3D-PCR amplicons were TA-cloned into a pCR4 vector for sequencing analyses. For in vivo mutation, A3C with or without Hsp90 was cotransfected with an HBV-encoding plasmid into HepG2 cells. After 48-h transfection, HBV relaxed circular DNAs were isolated from HBV capsids in the cytoplasm. HBV DNAs in the region of 1380 to 1820 nt were amplified by PCR-94 °C followed by 3D-PCR at 88 °C. The resultant cellular 88 °C 3D-PCR amplicons were cloned for sequencing analyses in parallel with the in vitro samples. Thirty clones (n = 30) were randomly selected from each treatment for sequencing analyses. The C-to-T mutation distribution against the HBV corresponding cytidine site (reference to HBV V01460.1) and collective mutation frequencies for each treatment are graphically presented for (A) A3C in vitro; (B) A3C+Hsp90 in vitro; (C) A3C in vivo; (D) A3C+Hsp90 in vivo mutations. HBV, hepatitis B virus.