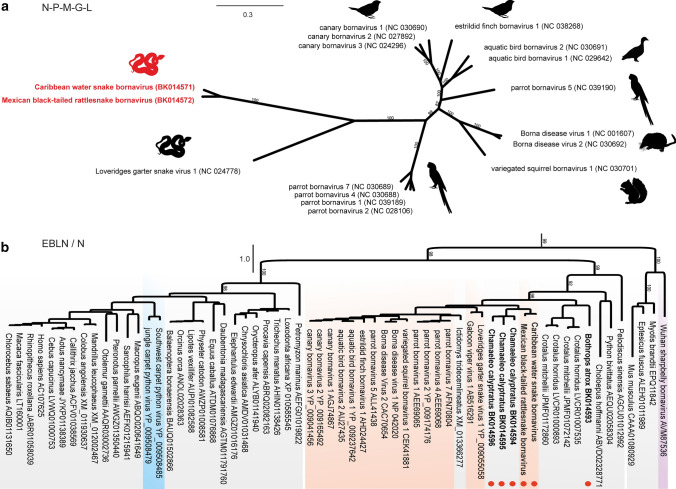
Fig. 2.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis of orthobornaviruses (a) and endogenous bornavirus-like nucleoproteins (b). (a) An unrooted phylogenetic tree based on the concatenated amino acid sequence alignments of N-P-M-G-L of the novel snake bornaviruses (highlighted in red) together with all available complete genome sequences of members of the genus Orthobornavirus. (b) Phylogenetic relationship between endogenous bornavirus-like nucleoprotein amino acid sequences (grey) and those of members of the bornavirus genera Carbovirus (blue), Orthobornavirus (orange) and Cultervirus (purple). Sequences determined in this study are indicated by red dots. Trees were calculated using IQ-TREE (version 2.1.2; 1 million ultrafast bootstraps; optimal substitution model for each alignment/alignment partition). The bars represent amino acid substitutions per site, and numbers in italics indicate bootstrap support for the major branches.