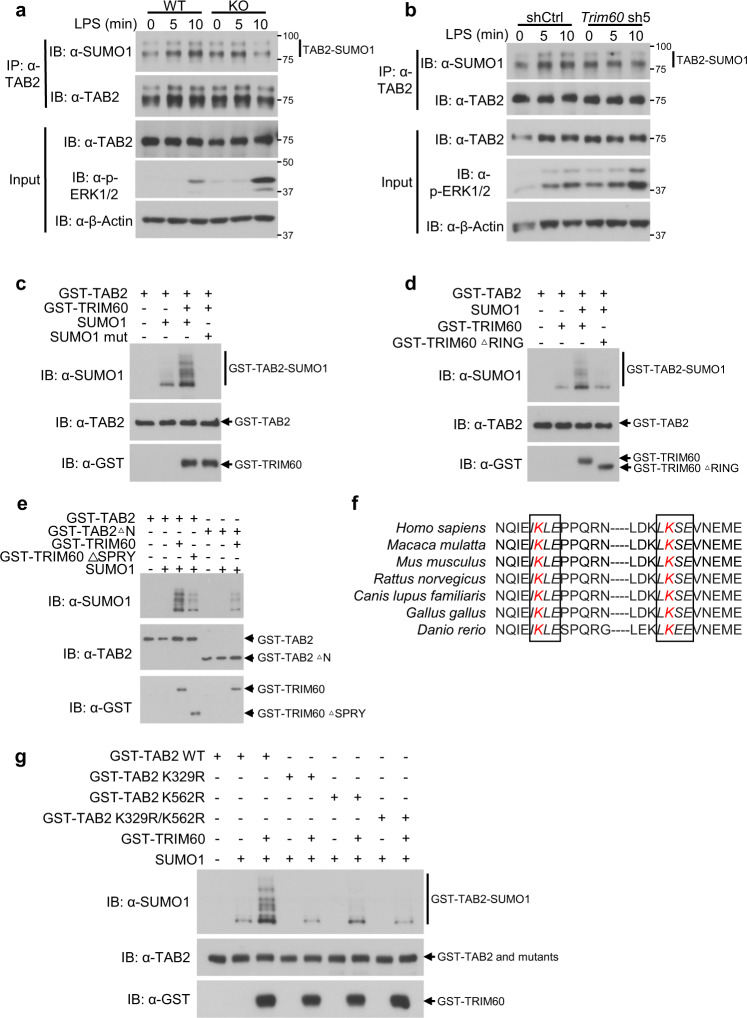
Fig. 4. TRIM60 mediates TAB2 SUMOylation.
IP and WB analysis of TAB2 SUMOylation. WT and TRIM60 KO BMDMs (a) or RAW cells infected with either control shRNA (shCtrl) or Trim60-shRNA #5 (Trim60 sh5) (b) were stimulated with LPS for the indicated time durations, followed by IP and WB analyses to examine TAB2 SUMOylation. The relative TAB2 SUMOylation levels (SUMOylated TAB2 vs total TAB2) in a and b were quantified by ImageJ and are shown as Supplementary Fig. 7a and b, respectively. c TRIM60 mediates TAB2 SUMOylation in vitro. GST-TAB2 and GST-TRIM60 were coincubated in vitro in the presence of the E1, E2, and SUMO1 proteins or the mutated SUMO1 protein (SUMO1 mut) at 30 °C for 3h. The samples were analyzed by WB with an anti-SUMO1 antibody. d GST-TAB2 was coincubated with either GST-TRIM60 or GST-TRIM60 ΔRING, and the SUMOylation of TAB2 was determined as described in c. e The TRIM60-TAB2 interaction is required for TAB2 SUMOylation. GST-TAB2, GST-TAB2 ΔN, GST-TRIM60, and GST-TRIM60 ΔSPRY were coincubated as indicated in the in vitro SUMOylation system in the presence of the E1, E2, and SUMO1 proteins, and WB was performed to examine TAB2 SUMOylation. f Two consensus SUMOylation motifs (ψ-K-X-E) in TAB2 are conserved among the detected species. The sequences in italics indicate conserved SUMOylation motifs of TAB2. g The K329R and K562R mutations abolished TAB2 SUMOylation mediated by TRIM60 as determined by in vitro SUMOylation analysis. The data are representative of three independent experiments (a–e, g)