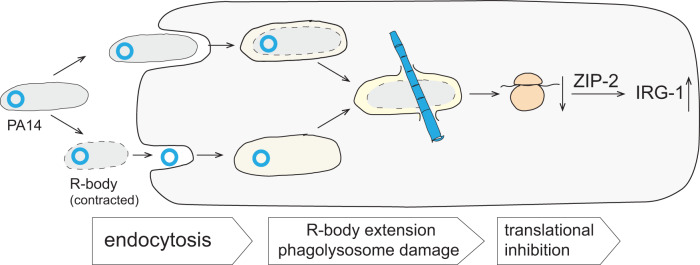
Fig. 8. Model of R-body action within a host cell.
R-body-containing P. aeruginosa cells, or contracted R-bodies themselves, are endocytosed by the host cell (e.g., a C. elegans intestinal cell). Conditions of the phagolysosome disrupt the integrity of the bacterial cell wall and/or trigger extension of the R-body. The R-body pierces the phagolysosomal membrane, releasing P. aeruginosa cell contents into the host cell cytoplasm. P. aeruginosa toxins and/or host responses to lysosomal disruption lead to cleavage of the C. elegans ribosome, translational inhibition, and, ultimately, host killing.