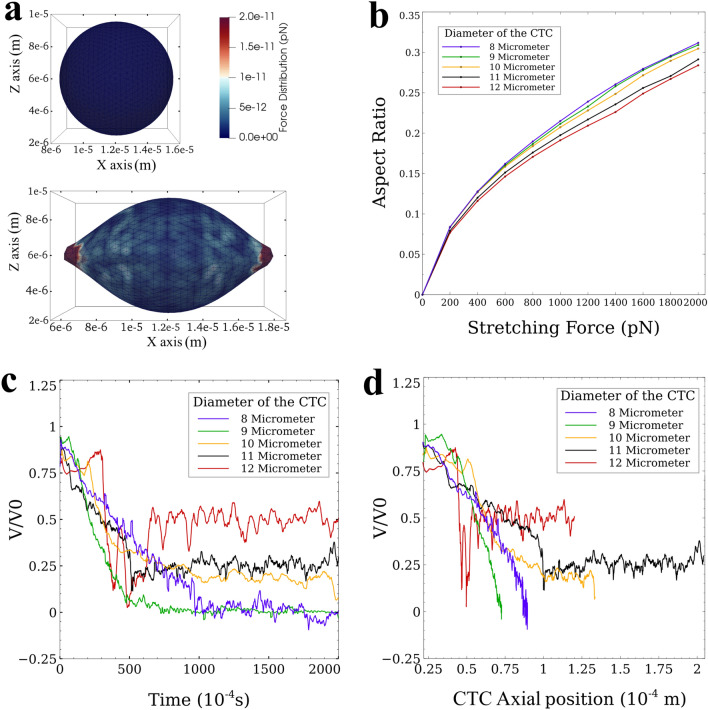
Figure 7.
Analysis of the effect of CTC diameter on its deformation and adhesion to the endothelial cells. (a) Stretch test simulation on CTCs with different diameters (Supplementary Table S1 of Supporting Information). Top: undeformed CTC; Bottom: CTC under tension force; (b) Aspect Ratio-Tension Force obtained from stretch test simulation. The variation in the mechanical deformation of the CTC with diameters ranging from 8 to 12 µm is within 10 percent; (c) Velocity–Time graph of the effect of size of the CTC with 5 attached platelets on its adhesion dynamics. CTCs with diameters equal or smaller than 9 µm form a firm adhesion with the vessel wall, but larger CTCs continue their rolling motion in the microvessel. The velocity of the rolling CTC also increases for larger CTCs; (d) Velocity–Axial Position graph of the effect of the CTC size on the rolling distance. The 9-µm CTC rolls a shorter distance than the 8-µm CTC does to form firm adhesion bonds. This is due to the ratio of the CTC diameter to the diameter of the vessel (124). CTCs with diameters larger than 9 µm continue their rolling motion (no firm adhesion observed for the length of simulation).