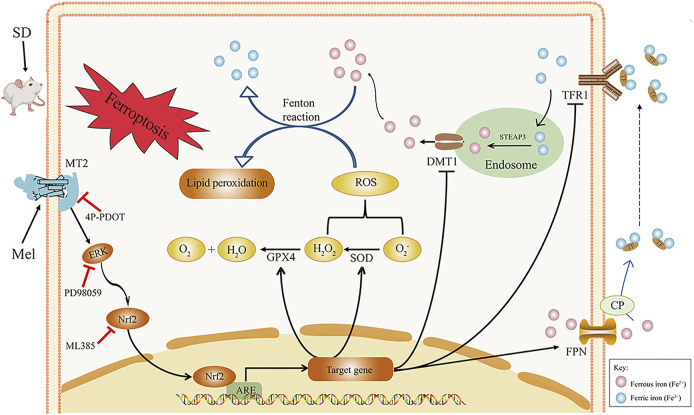
FIGURE 7.
Hypothetical diagram of how melatonin improves SD-induced hippocampal ferroptosis. Exogenous melatonin likely alleviates hippocampal ferroptosis caused by acute SD through by binding to the MT2 receptor and activating ERK/Nrf2 signaling, thereby improving lipid peroxidation and iron transporter disorder. ARE, antioxidant response element; CP, ceruloplasmin; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; ERK1/2, extracellular regulated protein kinases; FPN, ferroportin; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Mel, melatonin; ML385, Nrf2 inhibitor; MDA, malondialdehyde; MT2, melatonin receptor 2; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PD98059, ERK inhibitor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SD, sleep deprivation; SOD, superoxide dismutase; STEAP3, 6-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; 4P-PDOT, 4-phenyl-2-propionamidotetralin.