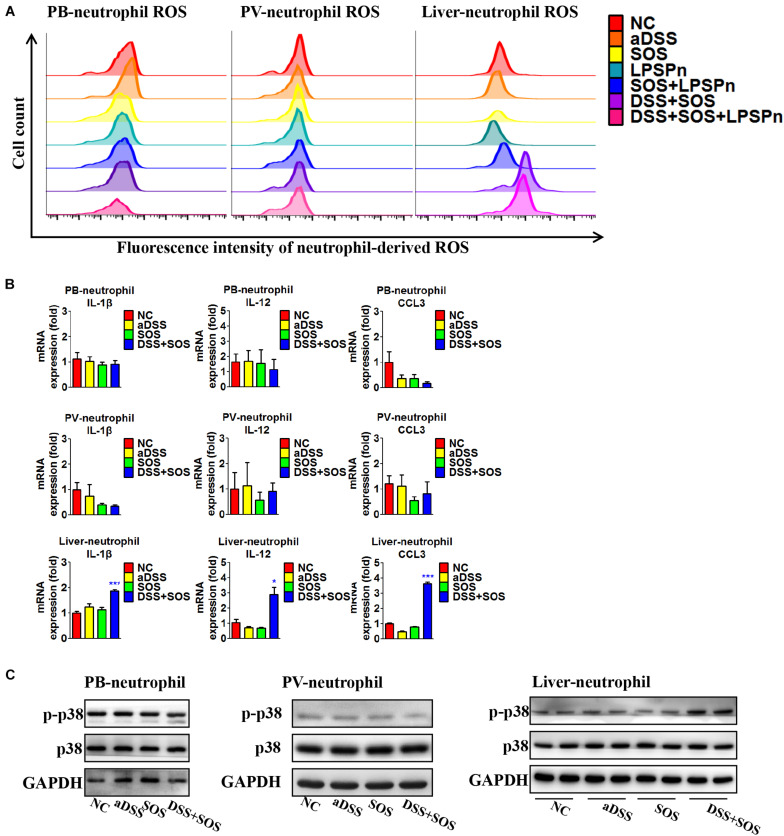
FIGURE 5.
In colitis-induced liver injury, neutrophils are activated in the liver. The activation status of neutrophils was evaluated via neutrophil-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS), neutrophil-derived cytokines, and phosphorylation of p38. (A) Neutrophil-derived ROS in the peripheral blood (PB), portal vein (PV), and liver were tested via flow cytometry in the following seven groups: normal control (NC), acute dextran sulfate sodium colitis (aDSS), sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS), lipopolysaccharide-induced pneumonia (LPSPn), SOS + LPSPn, DSS + SOS, and DSS + SOS + LPSPn. (B) Neutrophil-derived cytokines in the peripheral blood, portal vein, and the liver were evaluated in NC, aDSS, SOS, and DSS + SOS groups. (C) The phosphorylation of neutrophil p38 was also tested in the peripheral blood, portal vein, and liver. Asterisk indicates that the level is significantly different with normal control. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 by t-test; n = 5–6 per group; panels A and B are representative of three experiments; panel C is representative of two experiments.