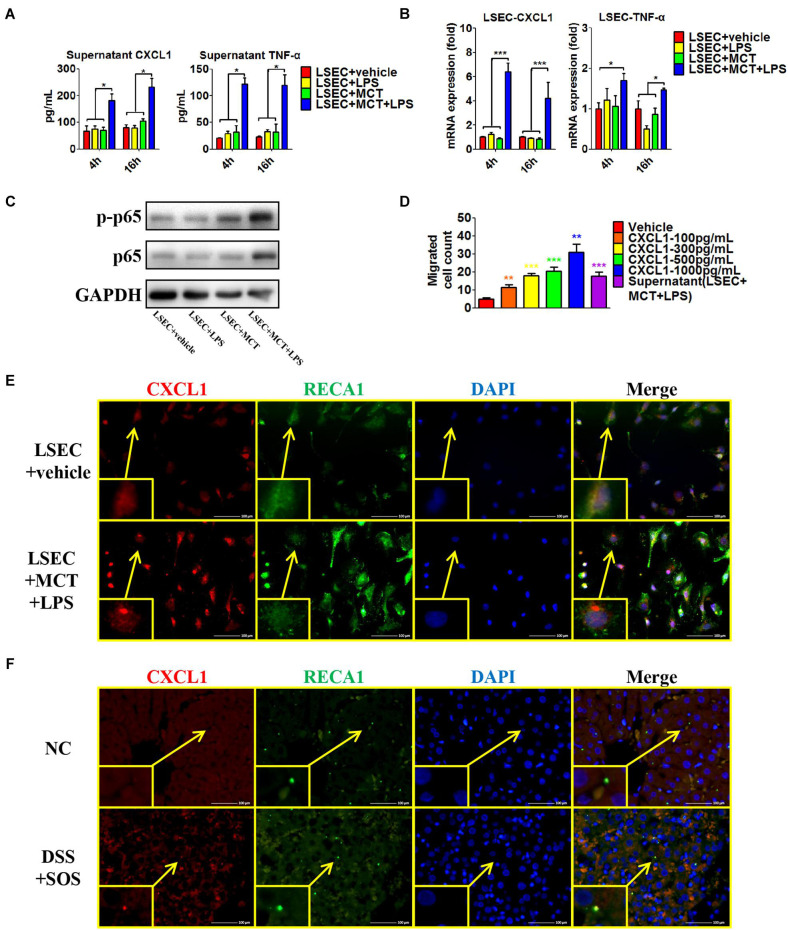
FIGURE 6.
Pro-inflammatory phenotype of damaged LSECs. After LSECs were treated with different stimuli [vehicle, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), monocrotaline (MCT), and MCT + LPS], the following parameters were examined: (A) the supernatant CXCL1 and TNF-α, tested by ELISA; (B) mRNA levels of CXCL1 and TNF-α; (C) phosphorylation of LSEC p65. (D) The influence of CXCL1 on neutrophil chemotaxis was evaluated by the number of trans-membrane migrated neutrophils in the Transwell experiment. (E) LSEC-derived CXCL1 was also examined by immunocytochemistry of CXCL1 (red) and RECA-1 (green, a marker of rat endothelial cells). (F) The co-localization of CXCL1 (red) and RECA-1 (green) was detected by immunohistochemistry in colitis-induced liver injury. Asterisk indicates that the level is significantly different from normal control. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA; n = 6 in each group; panels (A–C) are representative of three experiments; panel (C) is representative of one experiment, while other panels are representative of three experiments.