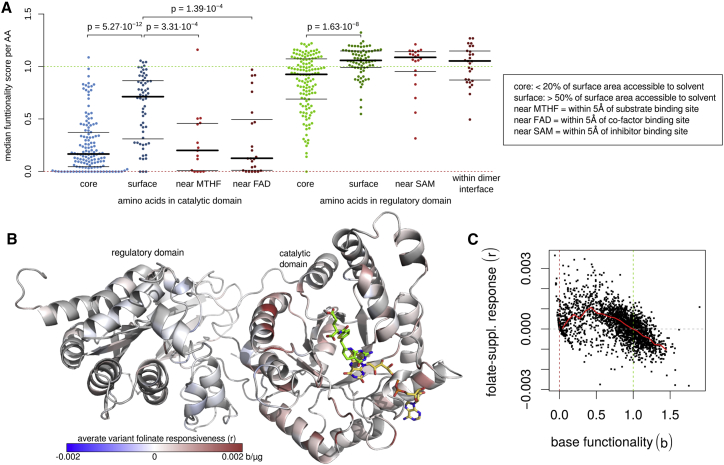
Figure 3.
Modeling folinate supplementation response and genetic interaction
(A) Median functionality scores of variants at amino acid positions with the following properties: (1) below 20% accessible surface area (ASA) in the catalytic domain; (2) above 50% ASA in the catalytic domain; (3) within 5Å of bound MTHF; (4) within 5Å of bound FAD; (5) below 20% ASA in the regulatory domain; (6) above 50% ASA in the regulatory domain; (7) within 5Å of bound SAH; (8) more than 20% ASA reduction when in dimer form. p values were calculated by Mann-Whitney U test. Thick and thin bars correspond to median, upper, and lower quartiles, respectively.
(B) Structure visualization of MTHFR with residues colored according to the average intensity of significant folinate-responsive variants at each position. Red positions indicate a positive folinate response, blue positions indicate a negative folinate response, and white positions indicate no response. FAD and folinate are shown in yellow and green wireframe representations.
(C) Scatterplots comparing the maximum-likelihood model base functionality (bi) and folinate-supplementation response parameters for each variant. The red line shows a running median across the x axis (interval size 0.1); the dotted dark red, dark green, and gray lines indicate null-like functionality, WT-like functionality, and zero response, respectively.