Figure 2.
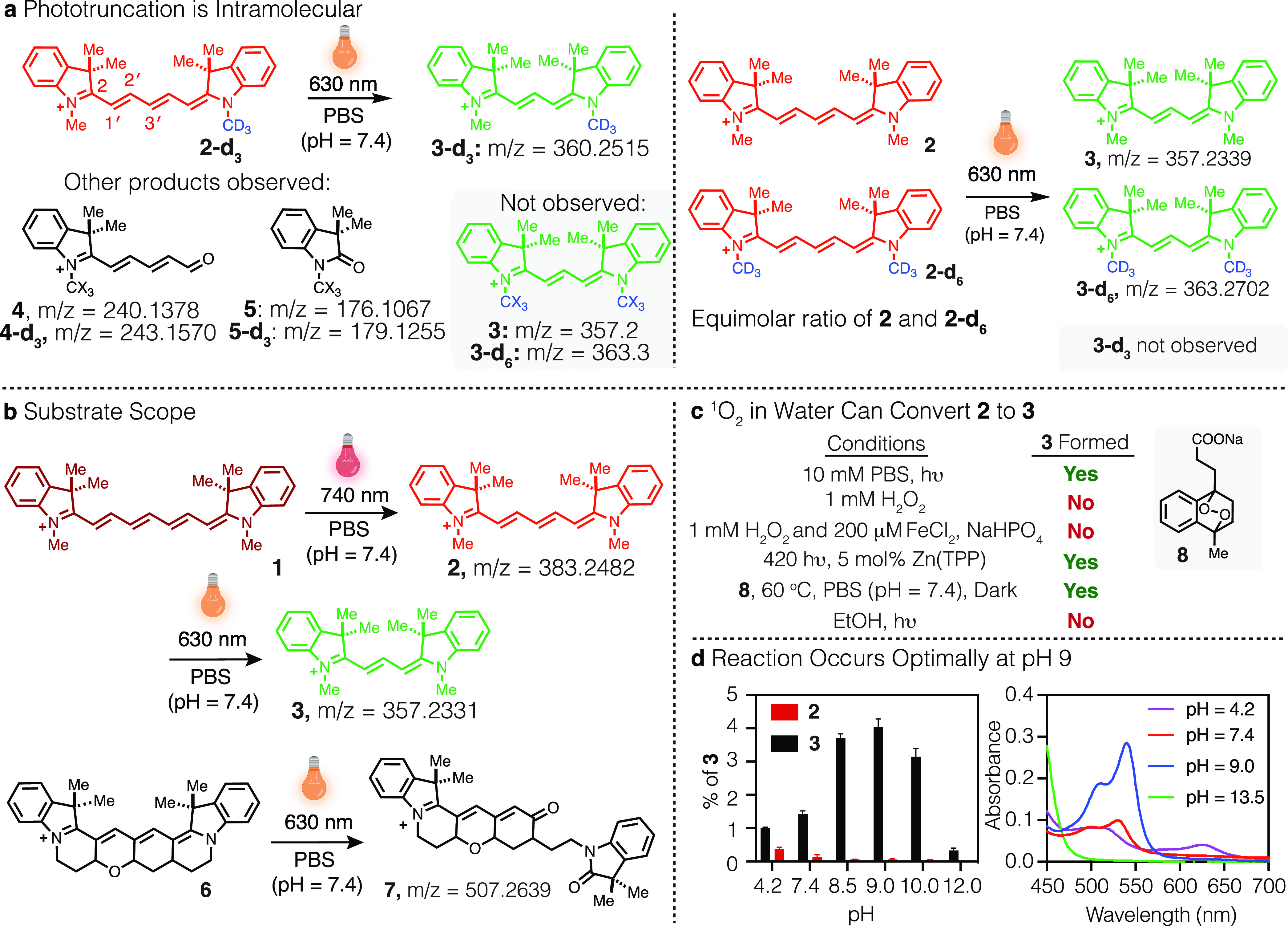
Mechanistic studies of cyanine phototruncation. (a) Products observed following irradiation of 2-d3 or an equimolar ratio of 2 and 2-d6 in PBS (100 μM, 1 mL, with 0.01% DMSO, pH = 7.4) with 630 nm LED at 0.2 W cm–2 for 60 min and monitored by HRESIMS. (b) Evaluating the scope of cyanine phototruncation in PBS (100 μM, 1 mL, with 0.01% DMSO, pH = 7.4) upon irradiation of a heptamethine probe (1) with 740 nm LED (at 0.5 mW cm–2, 30 min) and pentamethine probes (2 and 6) with 630 nm LED (at 0.2 mW cm–2, 60 min). (c) Evaluating the truncation of 2 to 3 with independently generated ROS (see Methods for detailed experimental procedures). (d) Effect of pH on conversion of 2 (50 μM) to 3 in Britton–Robinson buffer (0.04 M boric acid, 0.04 M phosphoric acid, and 0.04 M acetic acid that has been titrated to the desired pH with 1 M sodium hydroxide) upon irradiation with 630 nm LED at 0.2 W cm–2 for 60 min and monitored by UV–vis. Yields were calculated based on the absorption coefficients (ε) of 2 (230 400 M–1 cm–1) and 3 (150 000 M–1 cm–1) in water. Experiments were conducted in triplicate with the error expressed as the standard deviation of the mean.
