Fig. 3.
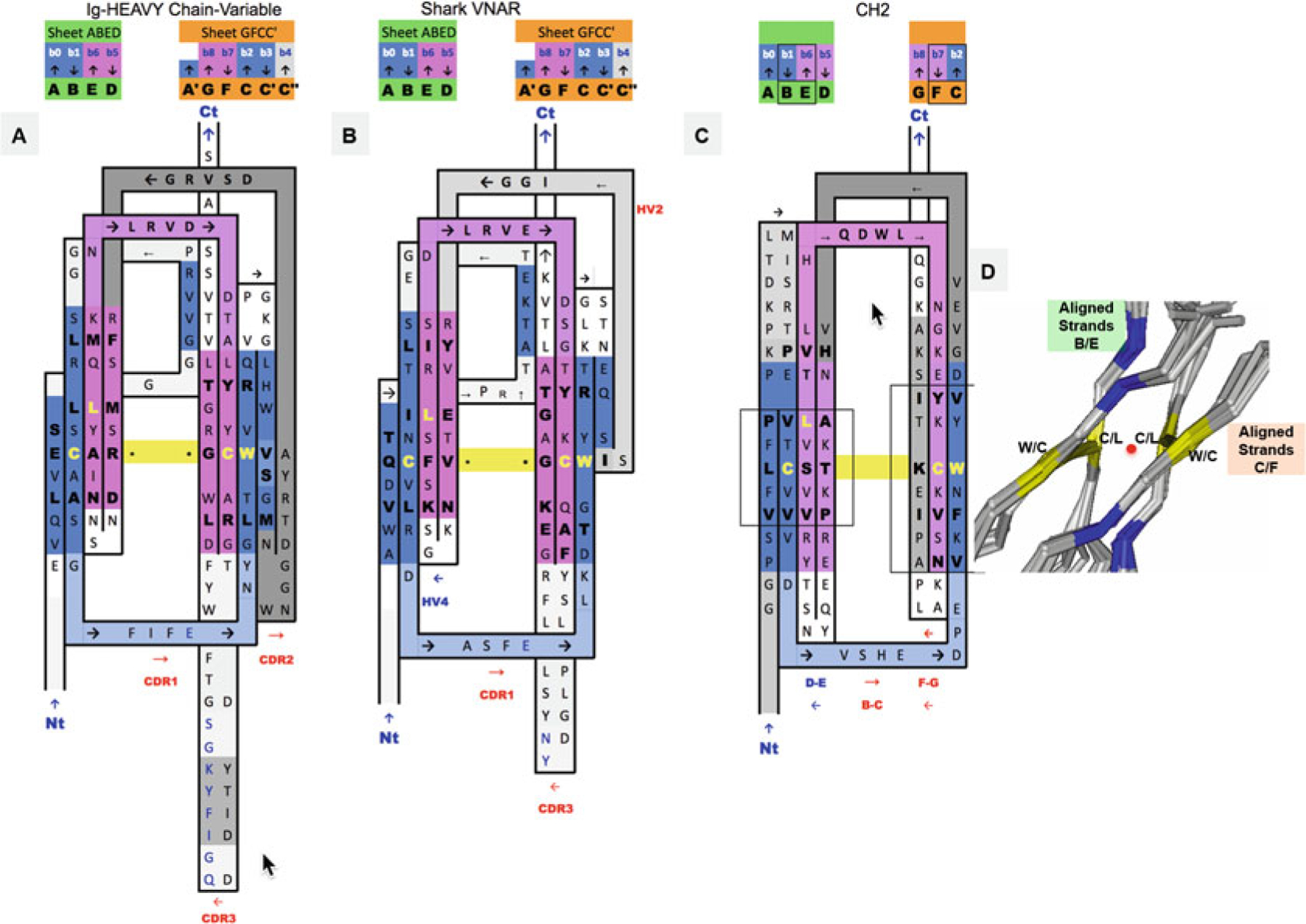
2D Sequence/topology maps of Ig domain topologies for IgV, Shark VNAR, and IgC. (a–c) Corresponding to schematic topology drawing in Fig. 2 for IgV, VNAR, and IgC, respectively: Topology/sequence map alignments based on 3D structure domain- and protodomain-level alignments of a Human Antibody Fab 5ESV (chain H, IgV domain), Shark VNAR 1VES, and an CH2 domain-isolated 3DJ9 and/or in an Fc chain context 4N0U (chain E). (d) Central strands B/E on Sheet A (A|B||E|D) and on Sheet B (G|F||C|C′). Protodomain 1 = A|B − C(C′)/Protodomain 2 = D|E − F(G). From 3D structure 2ATP (see Fig. 5) of CD8ab. The exact same pattern is observed here in IgV, VNAR, and IgC. These are four invariant residues (L can vary somewhat and be replaced by another hydrophobic residue). The cystine bridge flanked by a tryptophan is a well-known pattern that in fact exhibits pseudosymmetry with the residues in symmetry equivalent positions: C Cys (Strand B) ⇔ L Leu (Strand E) and W Trp (Strand C) ⇔ C Cys (Strand F). (d) Within a domain C/L on Sheet A central strands B/E and W/C on Sheet B central strands C/F occupy symmetry equivalent positions. The symmetry axis, perpendicular to the beta sheets A and B and the plane of the paper, is represented by a red dot. In symmetric dimers the two C2 domain axes coincide. These schematic maps are idealized showing vertical strands. The two sheets forming the central barrel are actually tilted vs. each other (relative rotation of one domain vs. the other around the common domain-dimer symmetry axis). This is true of any beta strand in any barrel
