Fig. 8.
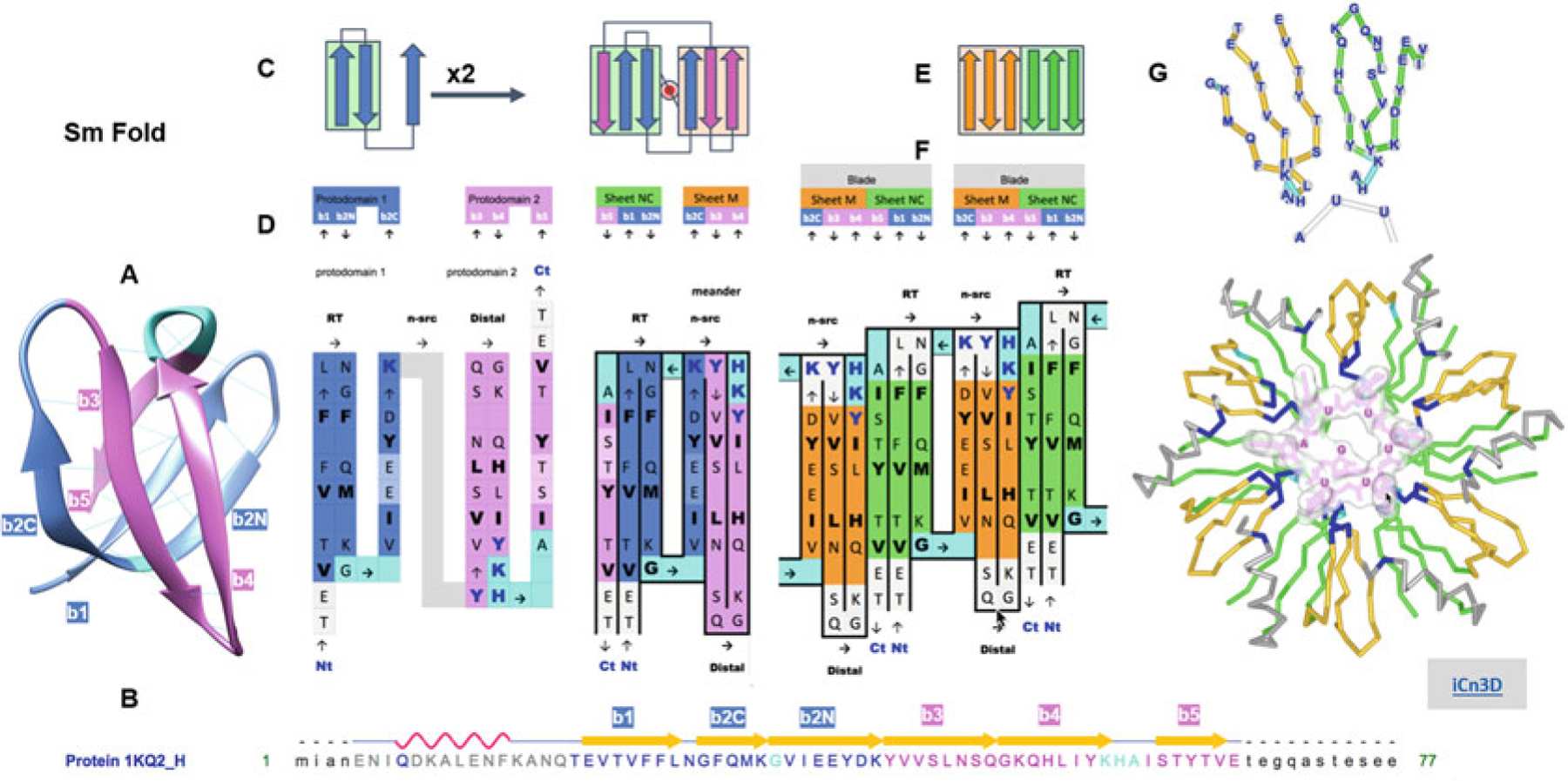
Complexity buildup through hierarchical symmetric arrangements of protodomains, domains, and oligomeric assemblies of the Sm fold (Hfq). (a) 3D structure of the bacterial Sm barrel (Hfq) (structure 1KQ2, N-terminal helix omitted for clarity). It is a small beta barrel with an SH3-like topology, usually considered as a five-stranded beta barrel (strands b1–b5). It is better represented as a six-membered barrel sandwich (splitting the long and sharply bent b2 strand in b2N and b2C at the Gly position, since b2N and b2C participate in two orthogonal sheets denoted either A and B or NC or M, as b1 and b5 N and C terminus come together in an antiparallel mode in the first sheet, vs. M a meander formed of b2C-b3-b4). Even a small barrel composed of 50 residues can exhibit C2 symmetry, bringing down to 20–25 residues the protodomain size with a bb-b topology formed by a hairpin b1|b2N-b2C. An SH3- topology, for SH3-like domains as for the Sm fold, is equivalent to short Greek key, with a simple Glycine in protodomain 1 and a 3–10 helix in protodomain 2 linking the two (orthogonal) sheets of the barrel. (b) Sequence and strand definition of an Hfq domain (1KQ2) with protodomain 1 in blue (res T20-K41) and protodomain 2 in magenta (res. Y42-E66). (c) 2D Schematic topology representation of protodomain and protodomain duplication with symmetric arrangement. (d) Sequence of two successive protodomains’ delineation and corresponding 2D topology/sequence map. Protodomain 1 in blue color, 2 in magenta. Linker residues G in protodomain 1 and YKHA (3–10 helix) in protodomain 2 are highlighted in cyan. Protodomains b1|b2N-b3 and b4|b5-b6 come together symmetrically with a b2C||b3 b5||b1 to form three-stranded Sheets A (green) and B (orange). Hydrophobic residues forming the core of the barrel are in bold black. RNA-binding residues are highlighted in dark-blue bold characters. (e) Schematic representation of the formation of a six-stranded blade from Sheet M (orange) and Sheet NC (green) of consecutive monomers. (f) “Quaternary” topology/sequence map of a dimer, with a b5||b4 quaternary interface. (g) A six-stranded blade representation in 3D labeled by sequence and the Hfq hexamer with RNA nucleotides binding at the interface between domains (RNA-binding residues highlighted in dark blue, as in (d)). All six strands can be considered calibrated with 5–6 residues (considering bulges, in the case of Sm in b2C and b5 symmetrically), so they form two calibrated three-stranded beta sheets that dock to form six-stranded blade, resulting in a six-bladed Hfq ring structure of C6 symmetry. A beautiful example of complexity buildup. Link to iCn3D: https://d55qc.app.goo.gl/pgk8GcZZNSs9KSMU6
