Fig. 2.
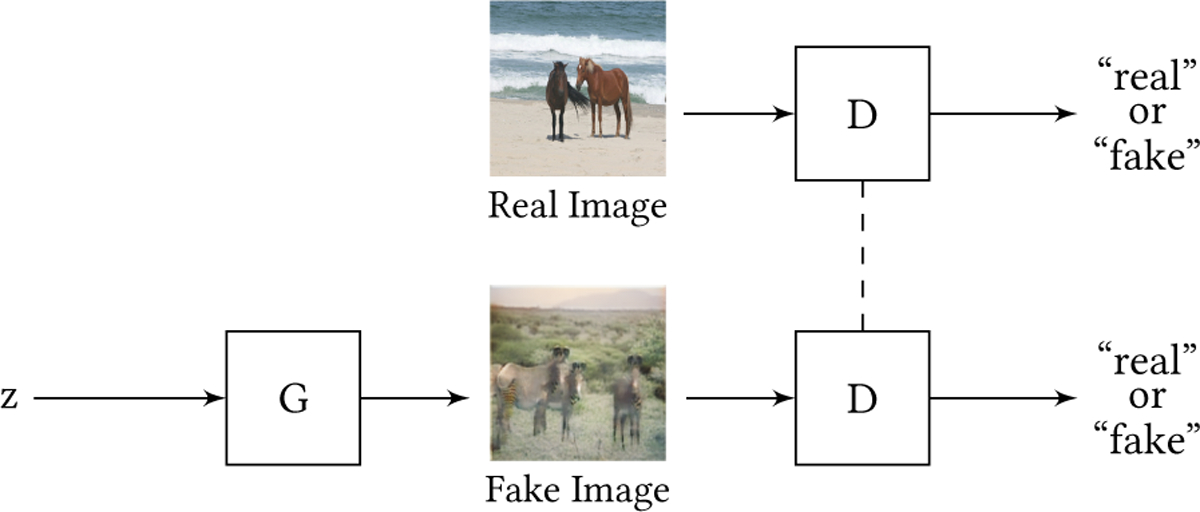
Illustration of the GAN generator G and discriminator D networks. The dashed line between the D networks indicates that they share weights (or are the same network). In the top row, a real image from the training data (horses ↔ zebras dataset by Zhu et al. [290]) is fed to the discriminator, and the goal of D is to make D(x) = 1 (correctly classify as real). In the bottom row, a fake image from the generator is fed to the discriminator, and the goal of D is to make D(G(z)) = 0 (correctly classify as fake), which competes with the goal of G to make D(G(z)) = 1 (misclassify as real).
