Scheme 1.
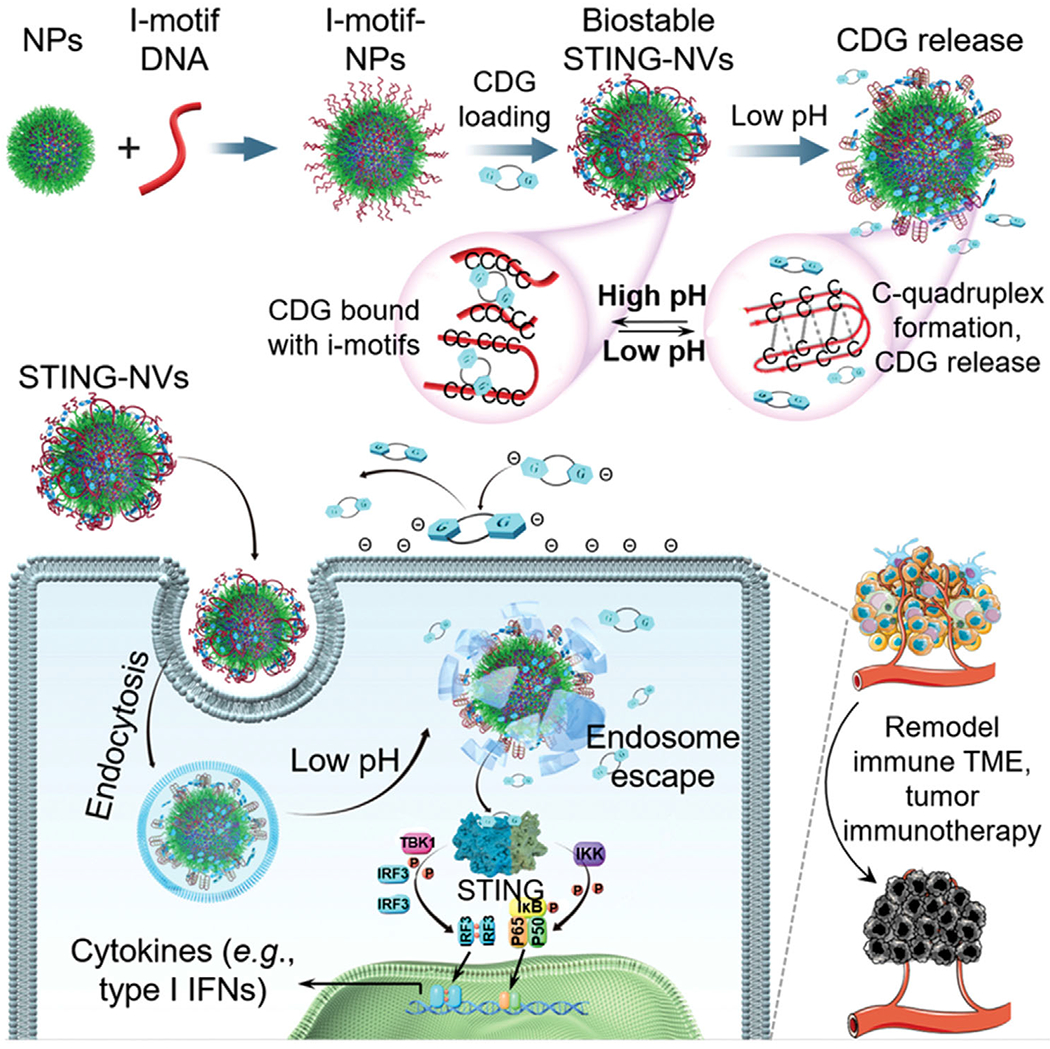
Schematic illustration of pH-responsive STING-NVs that efficiently load CDG at physiological pH, stabilized CDG, delivered CDG to immune cells, conditionally release CDG in the acidic endosome, and facilitated endosome escape of CDG for cancer immunotherapy. CDG was loaded in DNA i-motif-coated PEG-b-PLA NPs by hydrogen bonding (i.e., G:C base pairing) under physiological pH (linear i-motifs). Under acidic conditions such as immune cell endosome, i-motifs form C-quadruplexes through protonated C:C+ base-pair formation, leading to dissociation of CDG from i-motifs and hence CDG release from STING-NVs. TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; IRF3: interferon regulatory factor 3; IKK: Iκ B kinase.
