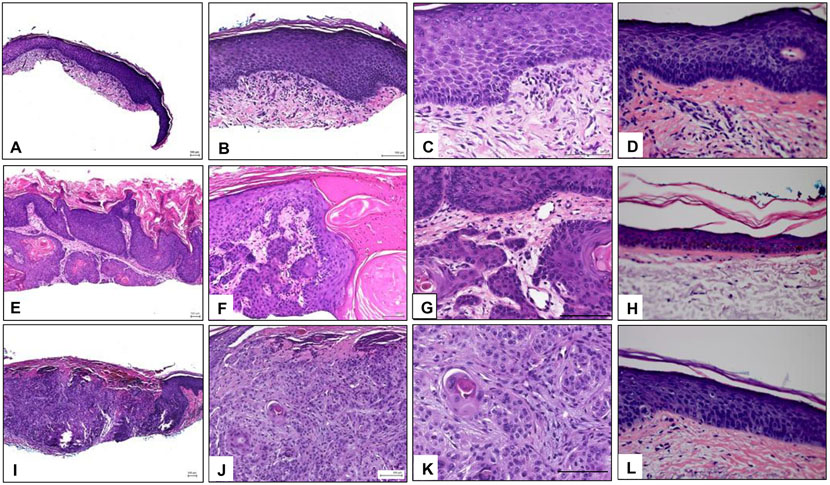
Figure 1.
Histopathology of representative samples. A-C) Images of a representative AK sample at 4x, 10x, and 20x, respectively, showing epidermal hyperplasia and dysplasia and marked hyper and parakeratosis with alteration of the ortho and parakeratotic keratin. The dermis shows solar elastosis and an infiltrate of mononuclear cells. D) Matched normal skin adjacent to the AK sample. E-G) Images of a representative KA sample at 4x, 10x, and 20x, respectively. Epidermis shows a crater-like invagination filled with ortho and parakeratotic horn. The lining of the invagination is formed by proliferating dysplastic squamous epithelium. H) Matched normal skin adjacent to the KA sample. I-K) Images of a representative SCC sample at 4x, 10x, and 20x, respectively. Arising from the epidermis and extending into the dermis there are aggregates of dysplastic keratinocytes. L) Matched normal skin adjacent to the SCC sample. AK: Actinic keratosis, KA: keratoacanthoma, SCC: squamous cell carcinoma.