Figure 1. Niraparib-resistant RPETP53−/−BRCA1−/− cell clones are cross-resistant to Olaparib and Talazoparib.
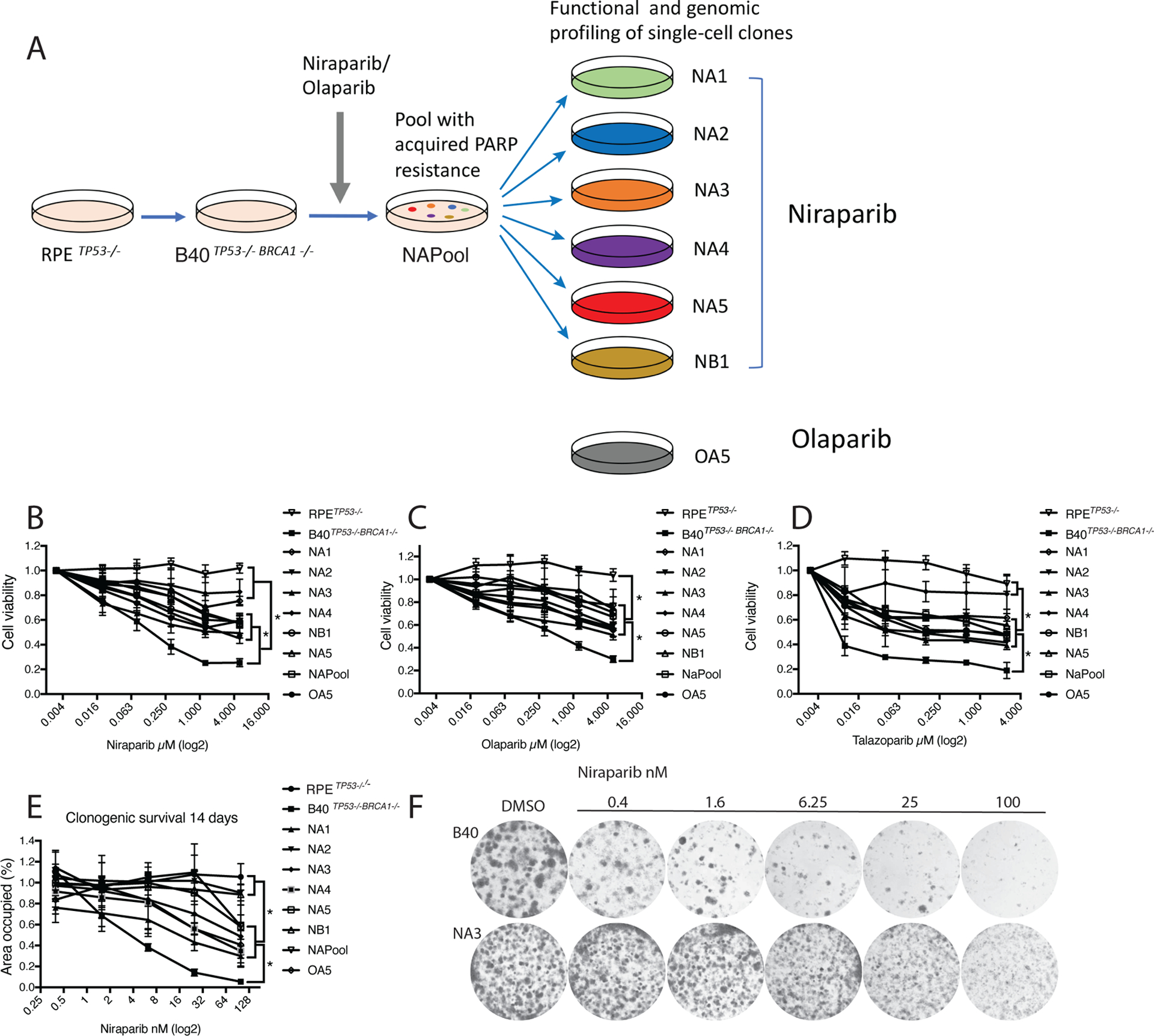
(A) RPETP53−/− and RPETP53−/−BRCA1−/− cells (B40) were generated using the CRISPR-Cas9 technology. A resistant cell line (NAPool) was generated by treating the B40 cell line with increasing concentrations of the PARP inhibitors Niraparib or Olaparib over three months. Next, we isolated single-cell clones from the Niraparib and Olaparib resistant pools for functional and genomic profiling.
(B) Resistance of these cell clones to Niraparib was confirmed in a 7-day CellTiter-Glo survival assay. The groups were compared using Oneway Anova and Tukeys multiple comparison test.
(C) Cell clones were also resistant to Olaparib, and (D) Talazoparib in a 7-day survival assay.
(E) Resistance to Niraparib was further confirmed in long-term 14-day clonogenic assays.
(F) Representative photographs showing the clonogenic growth of the NA3 resistant clone in presence of Niraparib in comparison to the B40 sensitive cell line. *p<0.05
