Fig. 1. Inhaled IFNβ alleviated HDM-induced asthma in mice.
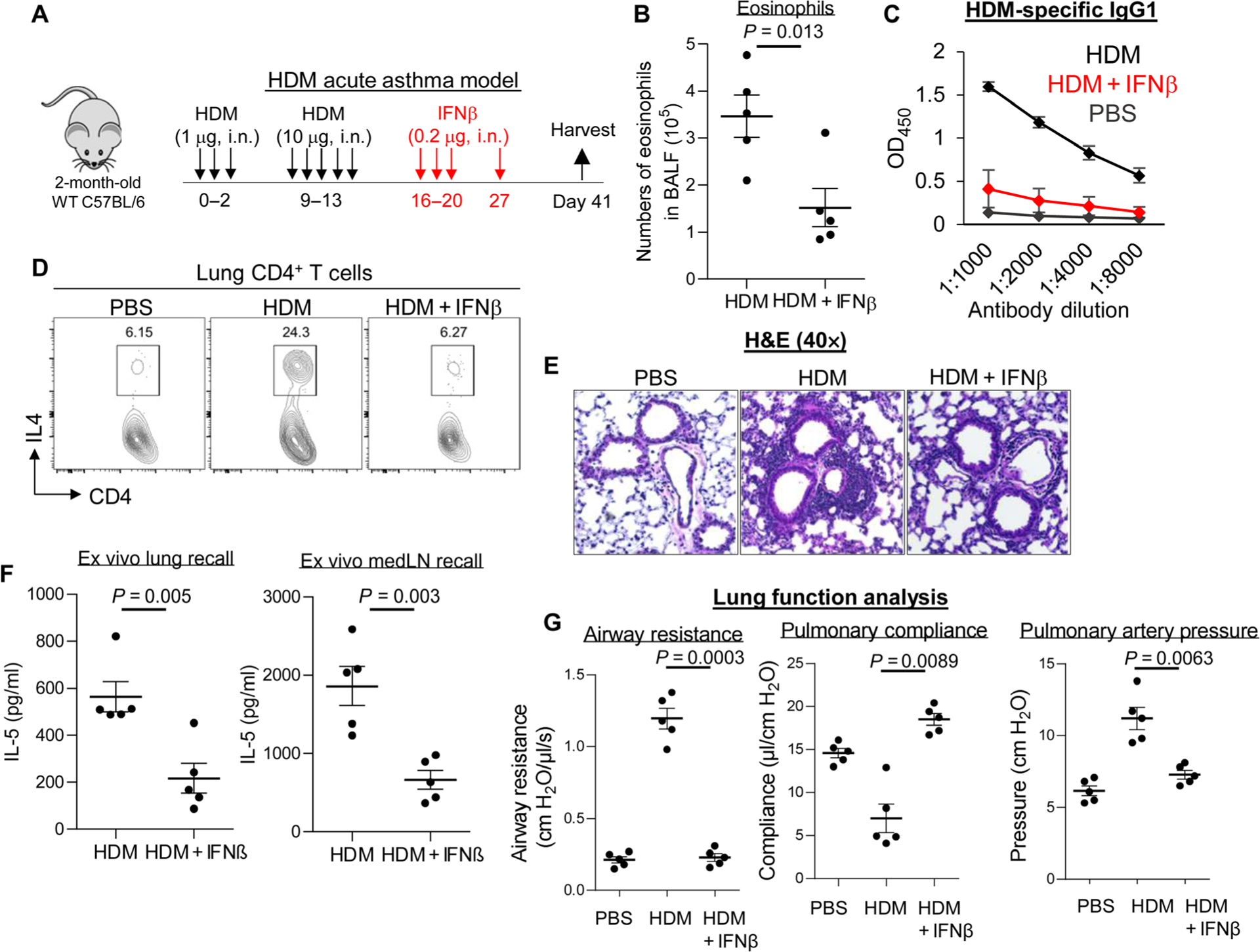
(A) Experimental protocol for HDM-induced acute asthma. Mice were intranasally (i.n.) administered PBS or IFNβ (0.2 μg). (B) Absolute numbers of BALF eosinophils of asthmatic mice treated with IFNβ (n = 3 to 7 mice per group). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Serum levels of HDM-specific IgG1 from asthmatic mice treated with IFNβ in (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Flow cytometry plots of IL-4–producing lung CD4+ T cells from asthmatic mice treated with IFNβ in (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Representative H&E staining of lung sections from asthmatic mice treated with PBS or IFNβ from (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (F) Cytokine production by lung and lung draining lymph nodes (mLNs) from asthmatic mice from (B) restimulated ex vivo for 4 days with HDM (25 μg/ml). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (G) Airway resistance, pulmonary compliance, and pulmonary artery pressure were determined in asthmatic mice as described in Materials and Methods (n = 3 to 5 mice per group). Data are representative of three independent experiments. Graphs represent the mean, with error bars indicating SEM. P values were determined by unpaired Student’s t test (B) and (F) or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (G). OD450, optical density at 450 nm.
