Fig. 6. Inhibiting FAO in TNFR2+ cDC2s reduced IFNβ efficacy in HDM-induced asthma.
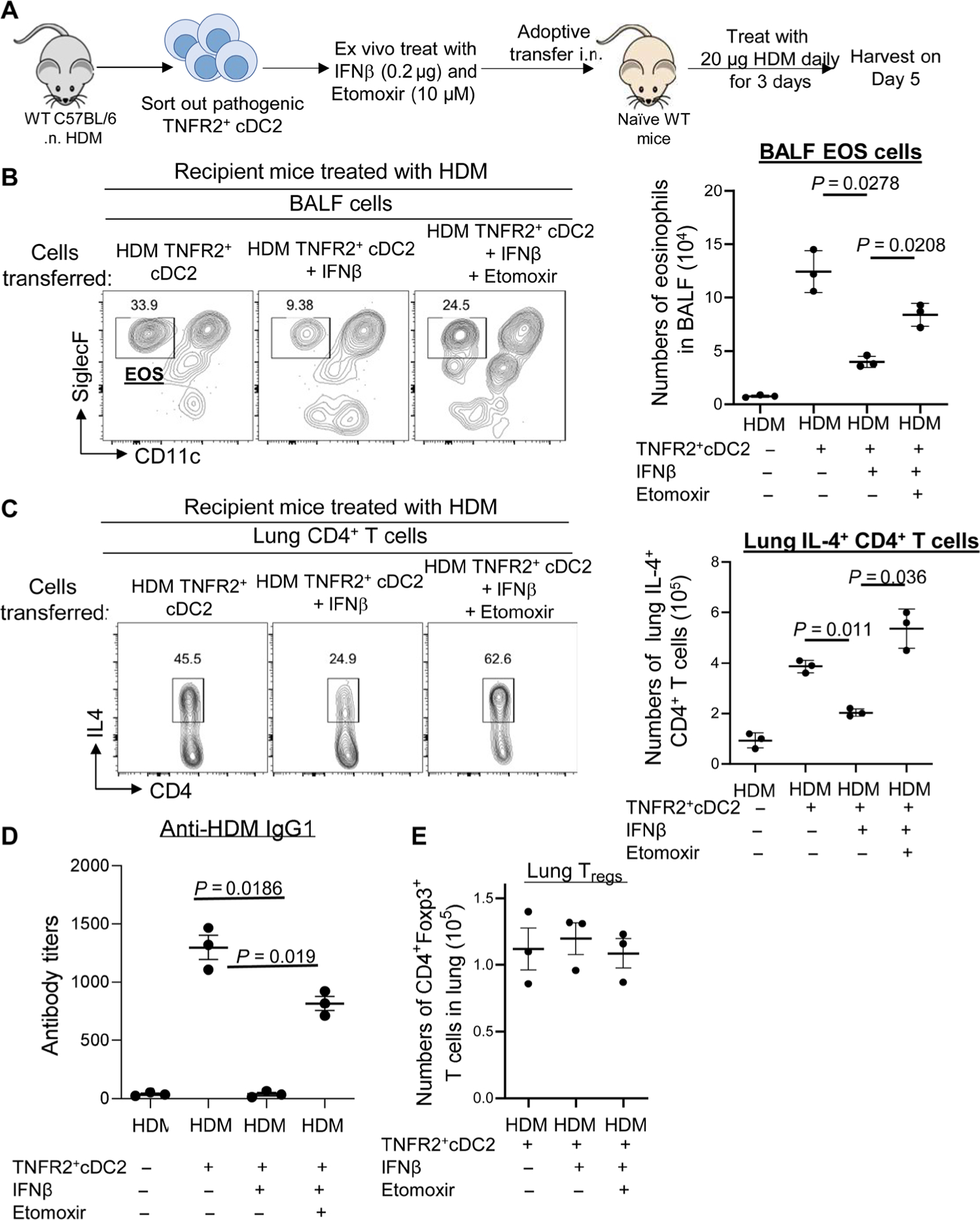
(A) Experimental design for adoptive transfer. TNFR2+ cDC2s cells were sorted out of WT mice 24 hours after treatment with HDM (100 μg). Sorted TNFR2+ cDC2s cells were treated with PBS, IFNβ (0.2 μg), and ETO (10 μM) for 30 min at 37°C. Sixty thousand treated TNFR2+ cDC2s cells were transferred intranasally into naïve C57BL/6J mice. Recipient mice were treated with 20 μg of HDM for three consecutive days. Mice were harvested 5 days after the last HDM treatment. (B and C) Flow cytometry analysis and total numbers of eosinophils (B) and IL-4 production by lung CD4+ T cells (C) in recipient mice (n = 3 mice per group). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Serum levels of HDM-specific IgG1 in recipient mice (n = 3 mice per group). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Total numbers of lung Tregs in recipient mice from (B) (n = 3 mice per group). Data are representative of two independent experiments. Graphs represent the mean, with error bars indicating SEM. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
