Fig. 3. ESX-1 and contact dependence of conjugal communication.
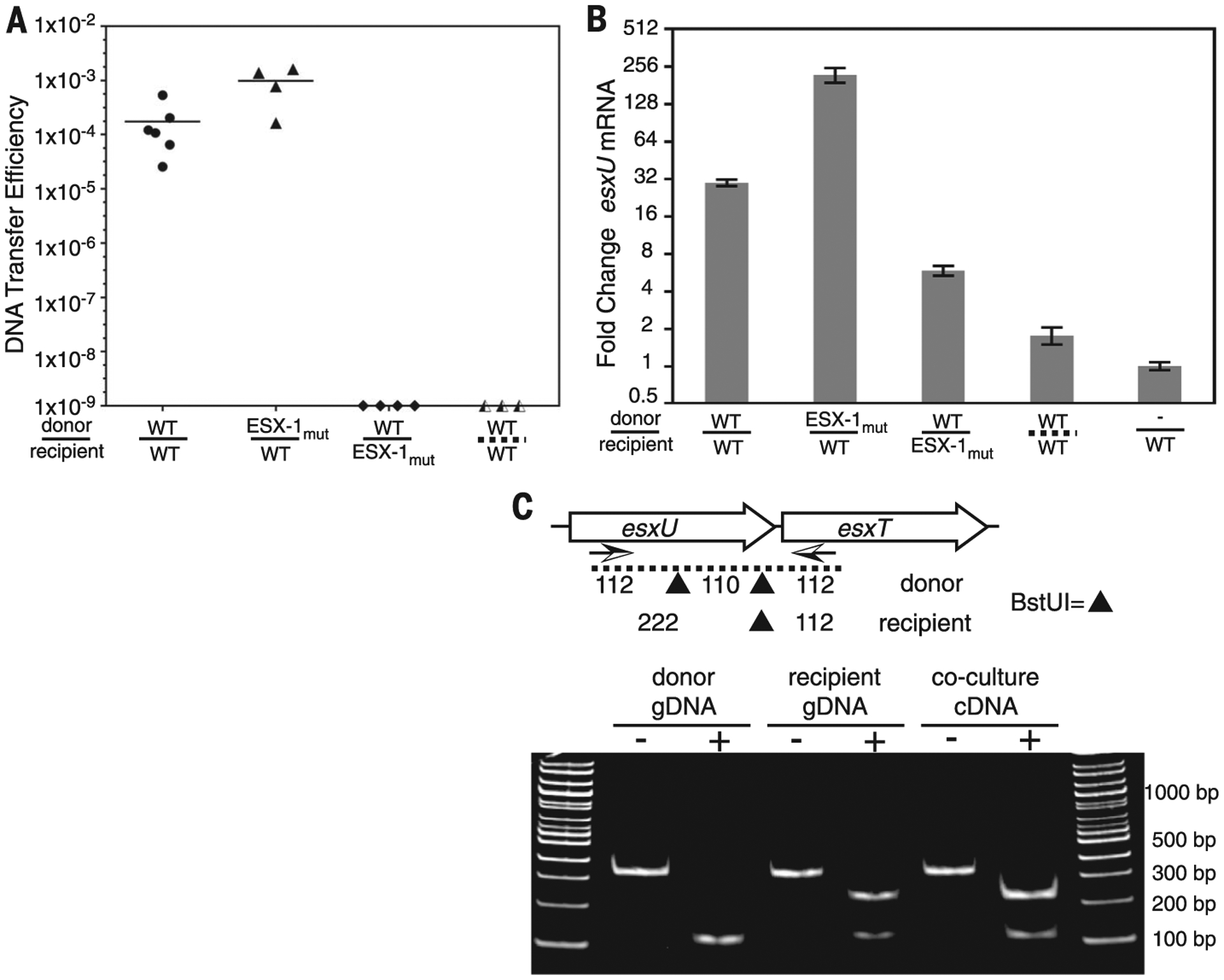
(A) DCT mating efficiencies for conjugal pairs used for RT-PCR. Strains are identified as WT or ESX-1mut (ΔeccCb1) donors (above the line) or recipients (below). The dashed line at bottom right indicates separation of conjugal strains by a porous membrane. (B) qRT-PCR analysis for esxU from cocultures of ESX-1 mutants or physically separated mycobacteria. esxU signals were normalized to rpoB expression. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3). (C) RT-PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of BstUI fragments identifies recipient origin of the elevated esxUT transcripts. Arrows below the genetic map indicate the primers used for amplification, and the sites of BstUI cleavage are indicated by triangles. Monoculture genomic DNA (gDNA) controls show the expected parental patterns upon digestion (+) with BstUI. Digestion of coculture-derived cDNA shows a recipient pattern. bp, base pairs.
