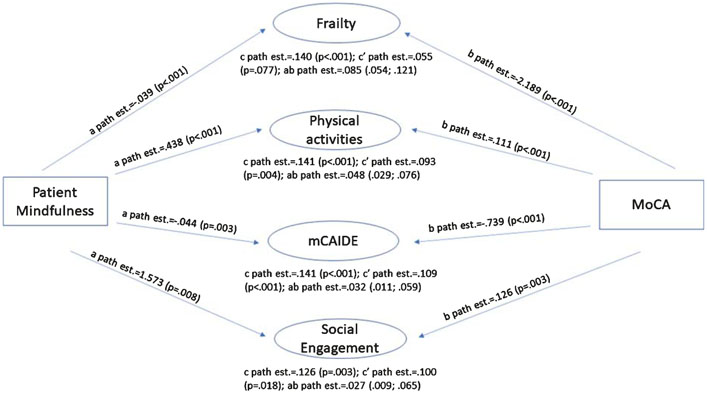
Fig. 2.
Mediation Analyses Patient Mindfulness and Global Cognition. Cross-sectional mediation analyses were employed to assess whether protective- and risk factors help explain at least in part the effect of patient mindfulness on cognitive function. Two resilience and two vulnerability factors were found to help explain the relationship between patient mindfulness and performance on the MoCA: physical activity as measured by the QPAR and socialization (resilience factors) and frailty as measured by the Fried Frailty Score and mCAIDE (vulnerability factors). Most path effects were significant at p < 0.001 indicating highly significant relationships between AMPS score, individual mediators, and MoCA. Higher levels of physical activity and socialization observed in participants high on mindfulness explained 34% and 21%, respectively, of AMPS positive impact on MoCA score. Similarly, lower frailty and mCAIDE scores explained 61% and 23%, respectively, of the effect of mindfulness on MoCA. See text for further details.