Figure 8.
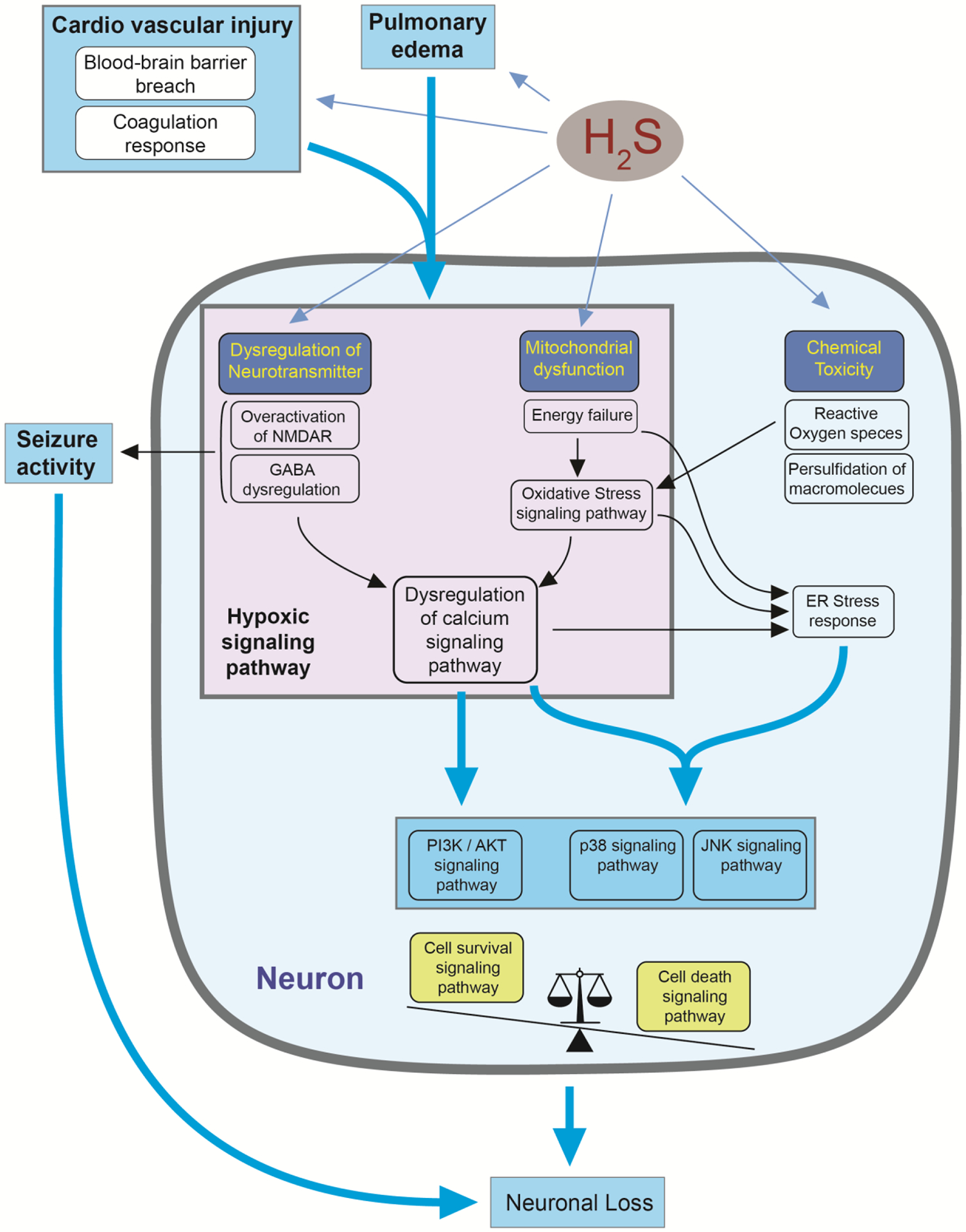
A hypothetical diagram summarizing the pathways leading to H2S-induced neuronal cell death. Hydrogen sulfide exposure induces dysregulation of multiple biological pathways leading to neuronal loss in the IC. Pulmonary edema and cardiovascular injury may reduce supply of oxygen, which may play a role in inducing the hypoxic signaling pathway. In addition, dysregulation of neurotransmitters such as NMDA and GABA and mitochondrial dysfunction may induce hypoxic signaling pathway, which may lead to calcium dysregulation and cell survival and death signaling pathways. Mitochondrial dysfunction and dysregulated calcium signaling may induce ER stress response and cell death signaling pathway. When cell death signaling pathway overcomes survival signaling pathway, neuronal loss may occur. Seizure activity derived from dysregulation of neurotransmitter system may further affect on neuronal loss.
