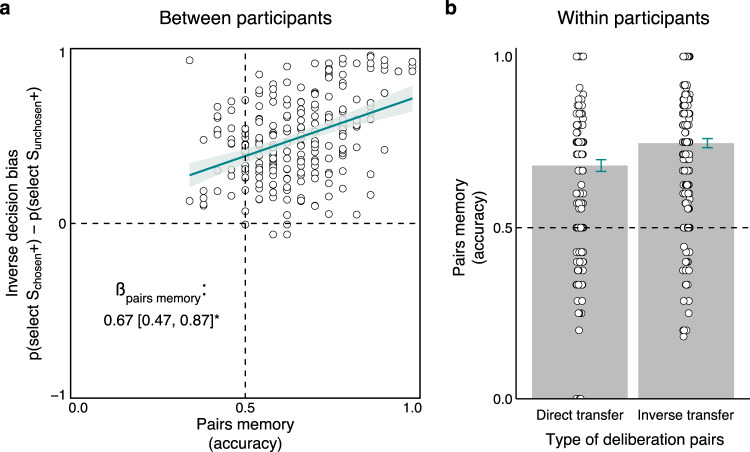
Fig. 3. Inverse inference of value is related to associative memory (Experiment 1, n = 235).
a The group-level inverse decision bias (difference in mean probability to choose rewarded items for chosen and unchosen pairs) is related to memory for the deliberation pairs. Points denote summarized observations of participants and the turquoise line denotes the fit of a Bayesian linear regression predicting inverse decision bias as a function of memory accuracy. Model fit and memory coefficient (beta) depict median and 95% highest density interval estimates. b The deliberation pairs were separated into two types for each participant based on outcome estimations (direct transfer: both the chosen and unchosen items within a pair were estimated with the same outcome, inverse transfer: the chosen and unchosen items were estimated to be in opposition). Pairs memory was better for inverse compared to direct transfer within participants. Points denote trial-averaged data of individual participants and error bars denote standard error of the mean. S+ denotes a rewarded stimulus (for unchosen stimuli, this is the outcome of their chosen counterpart). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.