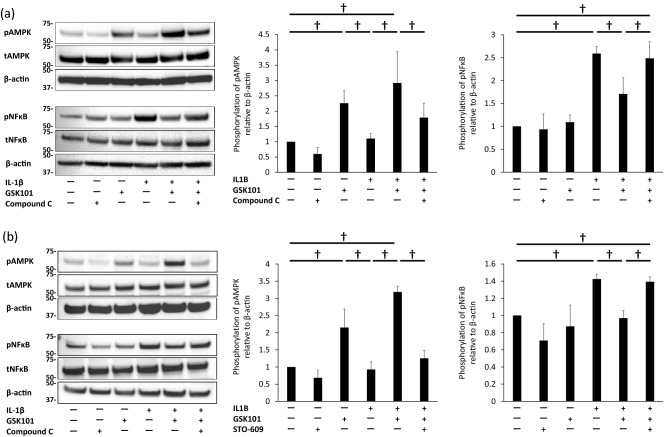
Figure 3.
Inhibition of NF-κB phosphorylation by activation of the CaMKK/AMPK pathway. Levels of pAMPK and pNF-κB in BACs treated with (a) IL-1β, GSK101, and Compound C (25 µM), and (b) IL-1β, GSK101, and STO-609 (5 µM) for 30 min, as assessed by Western blot. Experiments were repeated three times. Each group of pNFκB, tNFκB and β-actin was derived from the same membrane. Each group of pAMPK, tAMPK and β-actin was derived from the same membrane. The membrane associated with NFκB and the membrane associated with AMPK were different while their protein samples were the same. (a), (b) showed that stimulation with IL-1β for 30 min increased levels of pNF-κB, and GSK101 treatment for 30 min enhanced levels of pAMPK, compared with untreated control samples. (a) showed that pre-treatment with compound C significantly suppressed phosphorylation of AMPK and increased phosphorylation of NF-κB compared to cells treated with IL-1β and GSK101. (b) showed that pre-treatment with STO-609 for 1 h significantly suppressed phosphorylation of AMPK observed with the combination of GSK101 and IL-1β, and also countered the suppressive effect of GSK101 on IL-1β-induced NF-κB phosphorylation. ∫p < 0.05 compared to untreated control; †p < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; BAC: bovine articular cell; NFκB: nuclear factor kappa B; p-: phosphor-; t: total-.