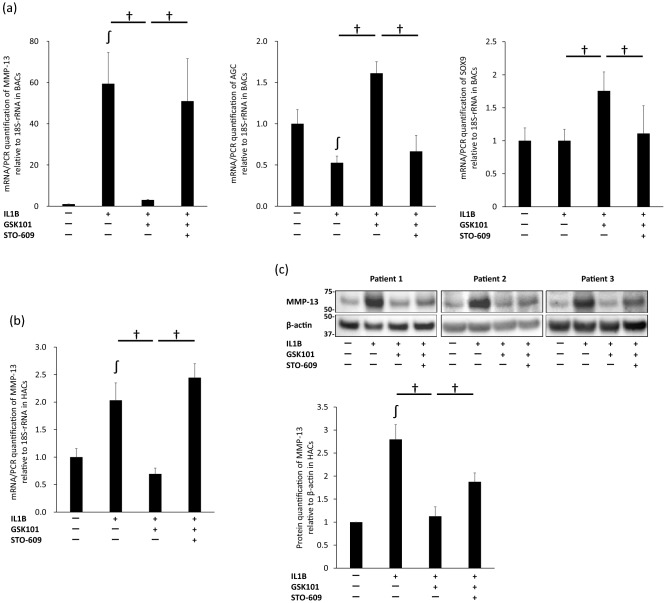
Figure 4.
Inhibition of IL-1β-induced cartilage damage via the TRPV4/CaMKK pathway. (a) Real-time PCR analysis of relative expression of MMP-13, AGC and SOX9 in BACs treated with IL-1β, GSK101, and STO-609 for 12 h. Pre-treatment with STO-609 canceled the suppressive effect of GSK101 on IL-1β-induced up-regulation of MMP-13 and down-regulation of AGC mRNA. Pre-treatment with STO-609 also canceled the suppressive effect of GSK101 on up-regulation of SOX9 mRNA. (b) Real-time PCR of relative expression of MMP-13 in HACs treated with IL-1β, GSK101, and STO-609 for 12 h, and (c) Western blot analysis of relative expression of MMP-13 in HACs treated with IL-1β, GSK101, and STO-609 for 48 h. (b), (c) showed that pre-treatment with STO-609 canceled the suppressive effect of GSK101 on IL-1β-induced up-regulation of MMP-13 mRNA and protein. Each experiment was repeated three times. Each group of the membrane associated with MMP-13 and the membrane associated with β-actin were different while their protein samples were the same. ∫p < 0.05 compared to untreated control; †p < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. BAC: bovine articular cell; CaMKK: calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase; HAC: human articular cell.