Figure 2 .
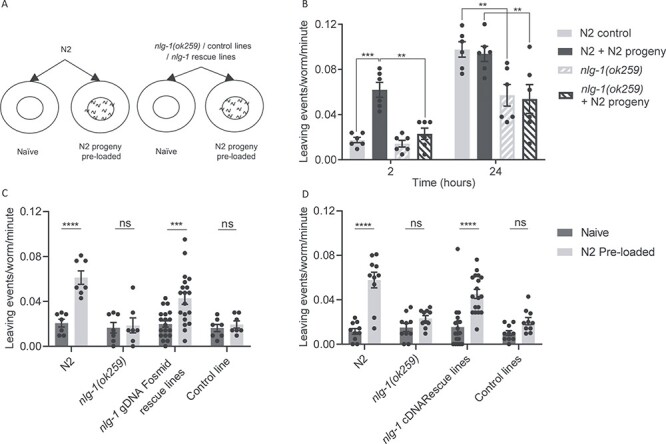
nlg-1(ok259) show a deficit in social interaction when exposed to N2 progeny. (A) Cartoon showing the principles of the pre-conditioned food-leaving assay. In order to test the effect of progeny on food-leaving behaviour, C. elegans adults were picked onto either a naïve or pre-conditioned food lawn. A naïve lawn contains no progeny whereas a pre-conditioned food lawn contains ~140 N2 progeny. (B) N2 and nlg-1(ok259) were picked onto naïve and pre-conditioned food lawns and their food-leaving behaviour observed at 2 and 24 h. N2 and nlg-1(ok259) n = 6. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. (C) The number of food-leaving events of N2, nlg-1(ok259), nlg-1 gDNA fosmid rescue nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [WRM0610dD09; Pmyo-3::gfp] and nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77; Pmyo-3::gfp] control adults on naïve and pre-conditioned food lawns. N2, nlg-1(ok259) and nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77; Pmyo-3::gfp] control line n = 7, nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [WRM0610dD09; Pmyo-3::gfp] n = 19. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test; ns P ≥ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. (D) The number of food-leaving events of N2, nlg-1(ok259), nlg-1 cDNA rescue nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77 (Pnlg1::nlg-1 Δ#14); Pmyo-3::gfp] and nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77; Pmyo-3::gfp] control line on naïve and pre-conditioned food lawns. N2, nlg-1(ok259) and nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77; Pmyo-3::gfp] control line n = 10. nlg-1(ok259) X, Ex [pPD95.77 (Pnlg-1::nlg-1 Δ#14); Pmyo-3::gfp] n = 18. Conditioning assays were performed as paired experiments and data obtained from independent replicas is presented. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; ns P ≥ 0.05, ****P ≤ 0.0001. All data shown as mean ± SEM
