Figure 5:
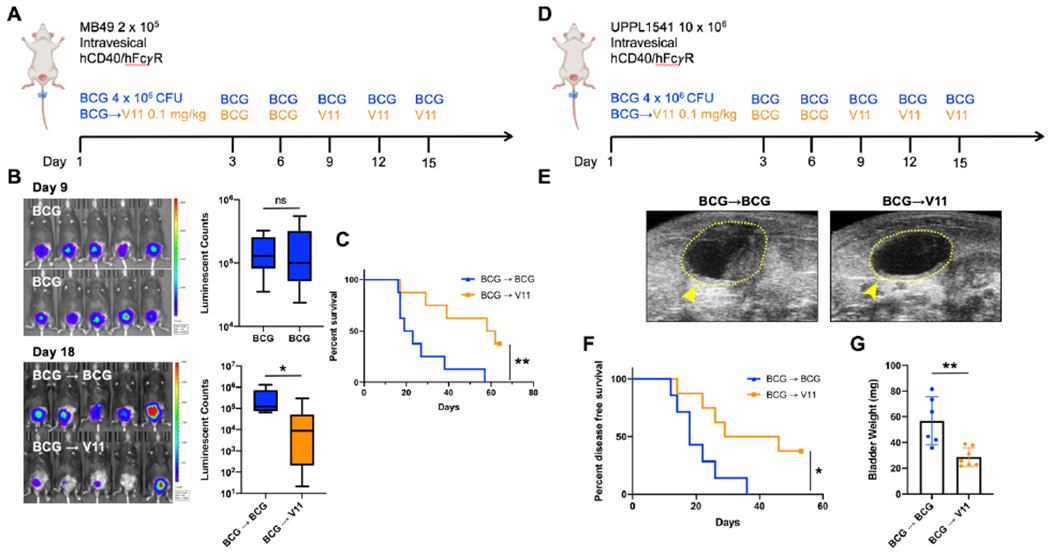
Intravesical Fc-enhanced anti-CD40 agonist antibody 2141-V11 induces tumor regression and improves survival in advanced BCG-unresponsive disease.
A, Schematic of orthotopic MB49 bladder tumor implantation and intravesical treatment with BCG and 2141-V11 (V11). Mice were initially treated with BCG beginning day 3 post tumor implantation, and those with progressive disease as assessed by tumor bioluminescence on day 9 were either continued on BCG (blue line) or switched to V11 treatment (orange line). B, Representative intravital luciferase imaging of the bladders of mice at day 9 post tumor implantation before continued BCG treatment or switch to V11 treatment. C, Quantification of bioluminescence data in B comparing the pre-V11 treatment tumor burden in both BCG continuation (n = 8 independent animals) and V11 (n = 8 independent animals) cohorts. D, Schematic of orthotopic UPPL1541 bladder tumor implantation and intravesical treatment with BCG and 2141-V11 (V11). Mice were initially treated with BCG beginning day 3 post tumor implantation, and at day 9 were either continued on BCG (blue line) or switched to V11 treatment (orange line). E, Representative ultrasound images on day 26 of mice continued on BCG treatment or switched to V11 beginning day 9. F, Disease-free survival of mice treated as outlined in E. Detection of enhanced contrast within the bladder space by serial ultrasound imaging was used to determine bladder tumor growth longitudinally. G, Bladder weights of mice treated as outlined in D were assessed at day 53 post tumor implantation. For B and G, Two-tailed t-tests were used to calculate statistical significance, n.s. = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. For C and F, Log-Rank test was used to calculate statistical significance, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
