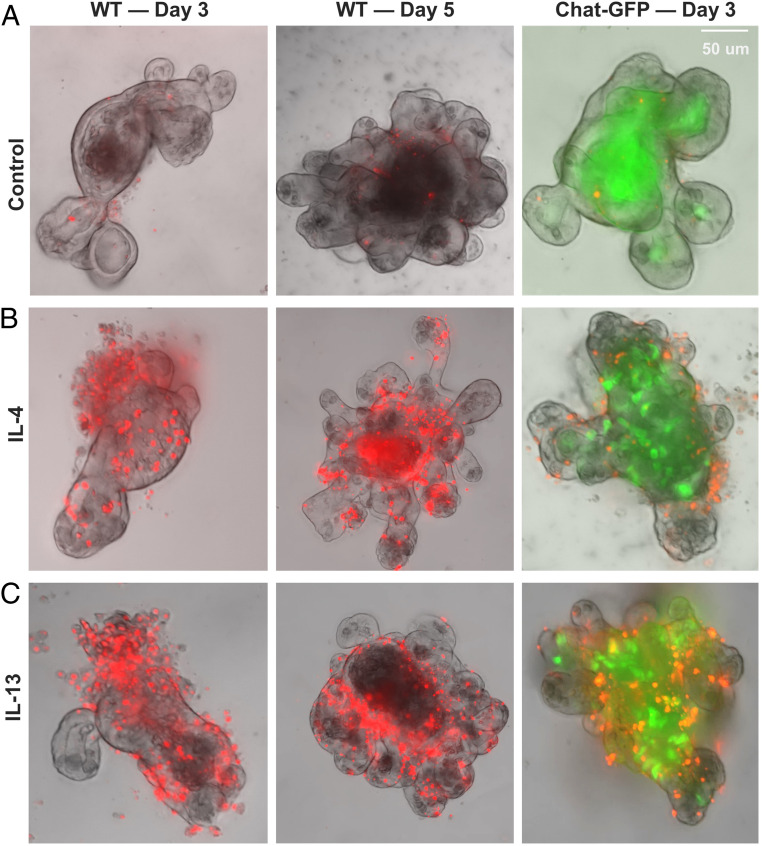
Fig. 4.
Lytic cell death in intestinal organoids treated with IL-4 or IL-13. Intestinal organoids generated from wild-type mice (Left and Middle) or ChAT-GFP mice (Right) were treated with IL-4 or IL-13 for 3 or 5 d and then assayed for the uptake of SYTOX orange. (A) Representative images of control organoids with no or few cells in the epithelial wall. Some cells in the organoid cores were dead cells that were shed and were labeled with SYTOX orange. (B) Representative images of organoids treated with IL-4. Multiple cells in the epithelial wall of organoids are labeled with SYTOX orange. (C) Representative images of organoids treated with IL-13. Multiple cells in the epithelial wall of organoids are labeled with SYTOX orange. The patterns of SYTOX orange staining in IL-13– and IL-4–treated organoids are similar. Note an increased number of tuft cells (ChAT-GFP, green) in IL-4– and IL-13–treated organoids that were generated from crypts of the small intestine of ChAT-GFP transgenic mice (B and C, Right). Experiments were repeated five or more times with similar results.