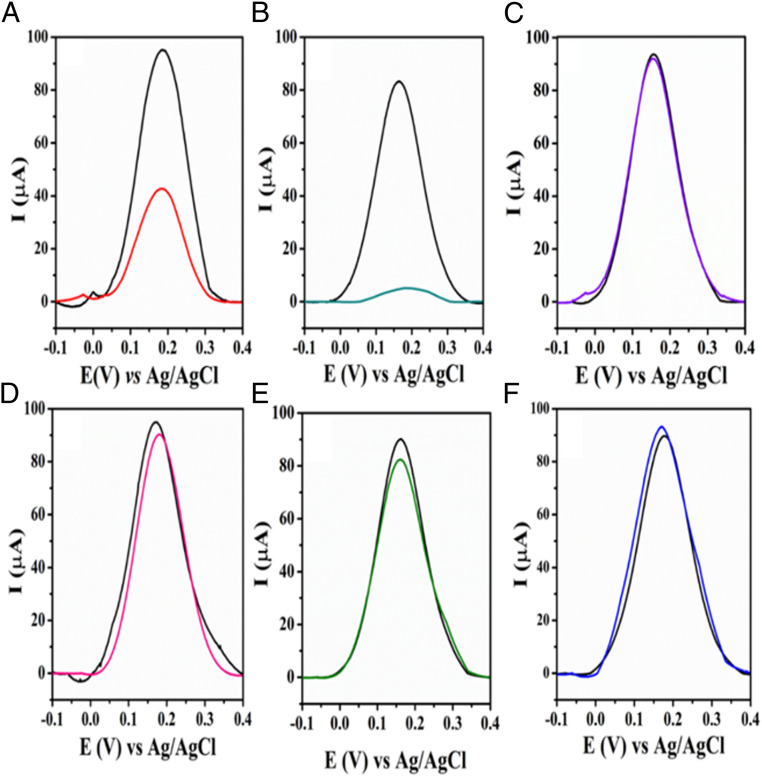
Fig. 5.
Cross-reactivity studies of LEAD using other coronaviruses and noncoronavirus strains. Baseline-corrected SWVs recorded at optimized experimental conditions before (black lines) and after incubation of the electrode with (A) SARS-CoV-2, (B) SARS-CoV-2 UK variant B, and possible interfering viruses such as (C) H1N1-A/California/2009, (D) Influenza-B/Colorado, (E) herpes simplex virus-2, and (F) MHV. The following conditions were used for all experiment: frequency of 80 Hz, amplitude of 70 mV, and step potential 8 mV. All experiments were performed in 5.0 mmol⋅L−1 [Fe(CN)6]−3/−4 in 0.1 mol⋅L−1 KCl. The specificity studies were carried out using the following viral strains: MHV at 108 PFU⋅mL−1 (coronavirus); H1N1, A/California/2009; Influenza B, B/Colorado; HSV2, and herpes simplex virus-2 (all at 105 PFU⋅mL−1). The analysis of the contagious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 UK variant showed that the variant presented higher interaction between SP and ACE2 compared to SARS-CoV-2. Each virus was incubated in a final volume of 50 µL for 5 min. All viruses were in stored VTM and experiments were performed at room temperature.