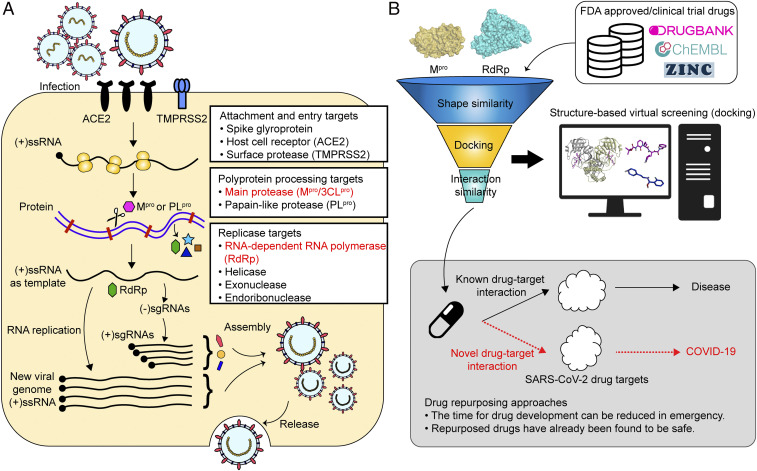
Fig. 1.
Drug targets against SARS-CoV-2 and computational drug repurposing strategy. (A) Potential drug targets in SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. Targets for viral attachment and entry include the viral spike glycoproteins, host receptors (ACE2), and proteases (TMPRSS2). Polyprotein processing can be targeted by inhibiting viral proteases such as main protease Mpro and papain-like proteases. Viral replicase-related enzymes are also attractive drug targets for antiviral activity. RdRp and helicase are important enzymes involved in the transcription and replication of SARS-CoV-2. Among these, the most important and less variable Mpro and RdRp were selected as drug targets in this study. (B) Docking-based virtual screening can identify novel compounds against targets of SARS-CoV-2 among the collection of approved and clinical trial drugs. Computational drug repurposing is an effective approach to identify novel drug-target interactions using the drugs already known to be safe, which provides the advantages of significantly reducing time for drug development and reduced failure rate.