Figure 2. Proposed physical models for enhancer-promoter communication.
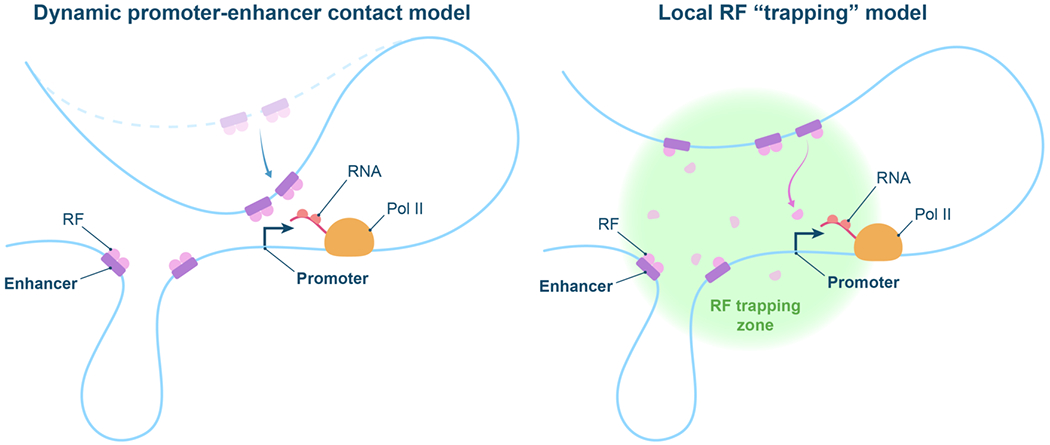
Dynamic P-E contact model: RFs stay mostly bound to cognate DNA and chromatin sites at the enhancers; RF interactions with the transcription machinery at the promoter are then facilitated by dynamic movements of the chromatin polymer that bring promoter and individual enhancers in molecular proximity. Local RF trapping model: P-E are staying at approximate proximity (100-200nm) while single RF molecules can dissociate from their DNA/chromatin sites and explore the local environment of the clustered enhancers, possibly through constrained motion, searching for the transcription machinery at the promoter.
