Figure 1: The four steps of molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis.
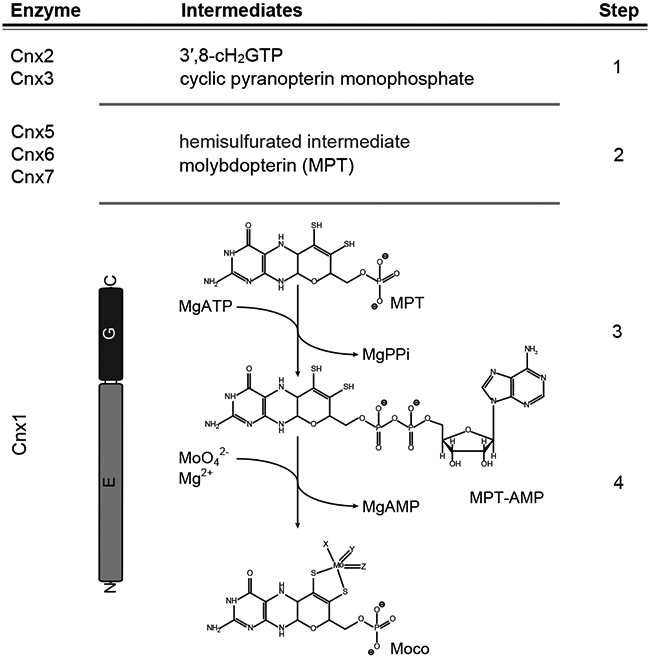
Schematic representation of the plant (Arabidopsis thaliana) molybdenum cofactor (Moco) biosynthesis pathway. The catalyzing enzymes and reaction intermediates are given. In the first step of the pathway, GTP is converted into 3′,8-cH2GTP14,15, which is subsequently turned over into cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate (cPMP16). cPMP is the substrate of the MPT-synthase complex (Cnx6 + Cnx712) catalyzing the formation of a hemisulfurated intermediate and finally molybdopterin (MPT)18. After each reaction cycle, the MPT synthase needs to be re-sulfurated19, which is catalyzed by Cnx5 in Arabidopsis12. MPT is a substrate of the molybdenum insertase (Mo-insertase) Cnx150. Here, the Cnx1-G domain catalyzes the formation of adenylated MPT (MPT-AMP26,27), which is used as the substrate for the E-domain catalyzed molybdate insertion25,26 and results in the formation of physiologically active Moco. Both the reaction mechanism describing molybdate insertion into the MPT dithiol and the first coordination sphere geometry of Moco following this last step in cofactor biosynthesis are unknown.
