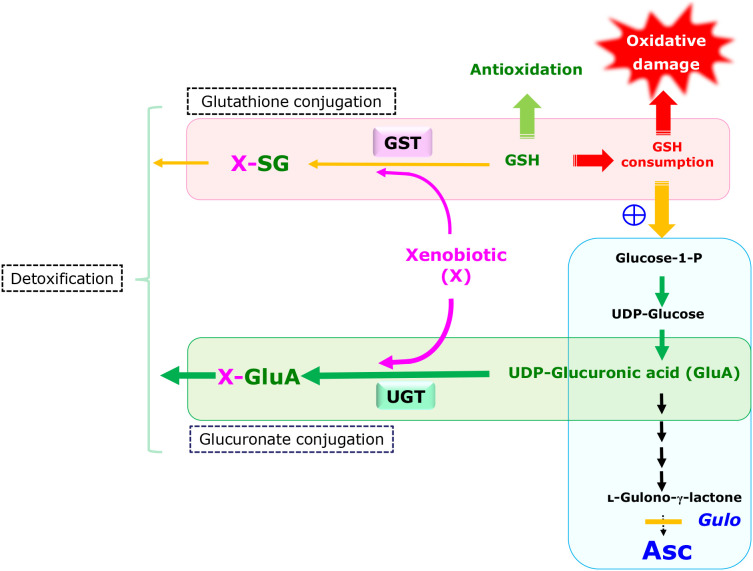
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of and crosstalk between two detoxification pathways, glutathione conjugation and glucuronate conjugation in the liver. While glutathione conjugation is catalyzed by glutathione S-transferases (GST), glucuronate conjugation is catalyzed by UGT. UGT may also catalyze the hydrolysis of UDP-glucuronate, resulting in the formation of d-glucuronate. Pathways for glucuronate conjugation and Asc synthesis share the metabolic processes up to UDP-glucuronate. Ablation of enzymes responsible for the downstream reaction causes the accumulation of intermediary compounds that include UDP-glucuronate. As a result, the glucuronate conjugation reaction is enhanced in animals that have a defect in Asc synthesis and preserve glutathione for antioxidation.