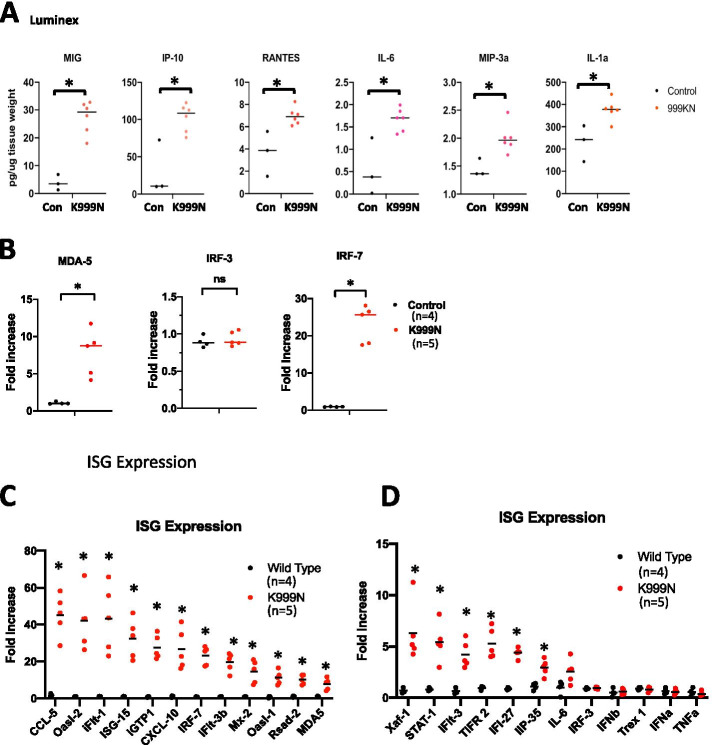
Fig. 5.
ADAR1K999N mutation results in increased ISG expression in the brain. A Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines were measured in the brain protein extracts using Luminex assays. The cytokine and chemokine levels were significantly increased in ADAR1K999N mice. n = 3 (wt, black dots) and 5 (K999N mutant, red dots), p = 0.024 (MIG), 0.020 (IP-10), 0.024 (RANTES), 0.020 (IL-6), 0.019(MIP-3a), and 0.048 (IL-1a), with statistical analyzed using Wilcoxon rank-sum test. B MDA-5, IRF3, and IRF5 expression in brain tissues of wild type and ADAR1K999N mice was quantified using a real-time PCR approach. MDA-5 expression is significantly increased in ADAR1 K999N mice, n = 4 (wild type), n = 5 (ADAR1K999N), *p < 0.05. While IRF-3 levels do not show a difference between the two groups, IRF-7 expression is more than 25 fold increased in ADAR1K999N mouse brain with comparison to the controls, n = 4 (wild type), n = 5 (ADAR1K999N), *p < 0.05, as analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. C, D Interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression in brain tissues of wild type and ADAR1K999N mice was quantified using a real-time PCR panel covering 24 ISGs. Within this panel, mRNA levels of 18 ISGs are significantly increased in ADAR1K999N mice, with 20- to 70-fold increase of the top 7 ISGs including CCL-5, Oasl-2, ifit-1, ISG-15, iGTP1, CXCL-10, and IRF-7. n = 4 (wild type), n = 5 (ADAR1K999N), *p < 0.05, with statistical analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The gene expression levels in B–D were calculated using the ΔΔt method with reference to the average of GAPDH and HRTP. Increases were expressed as fold changes relevant to levels in wild type mice