Fig. 1.
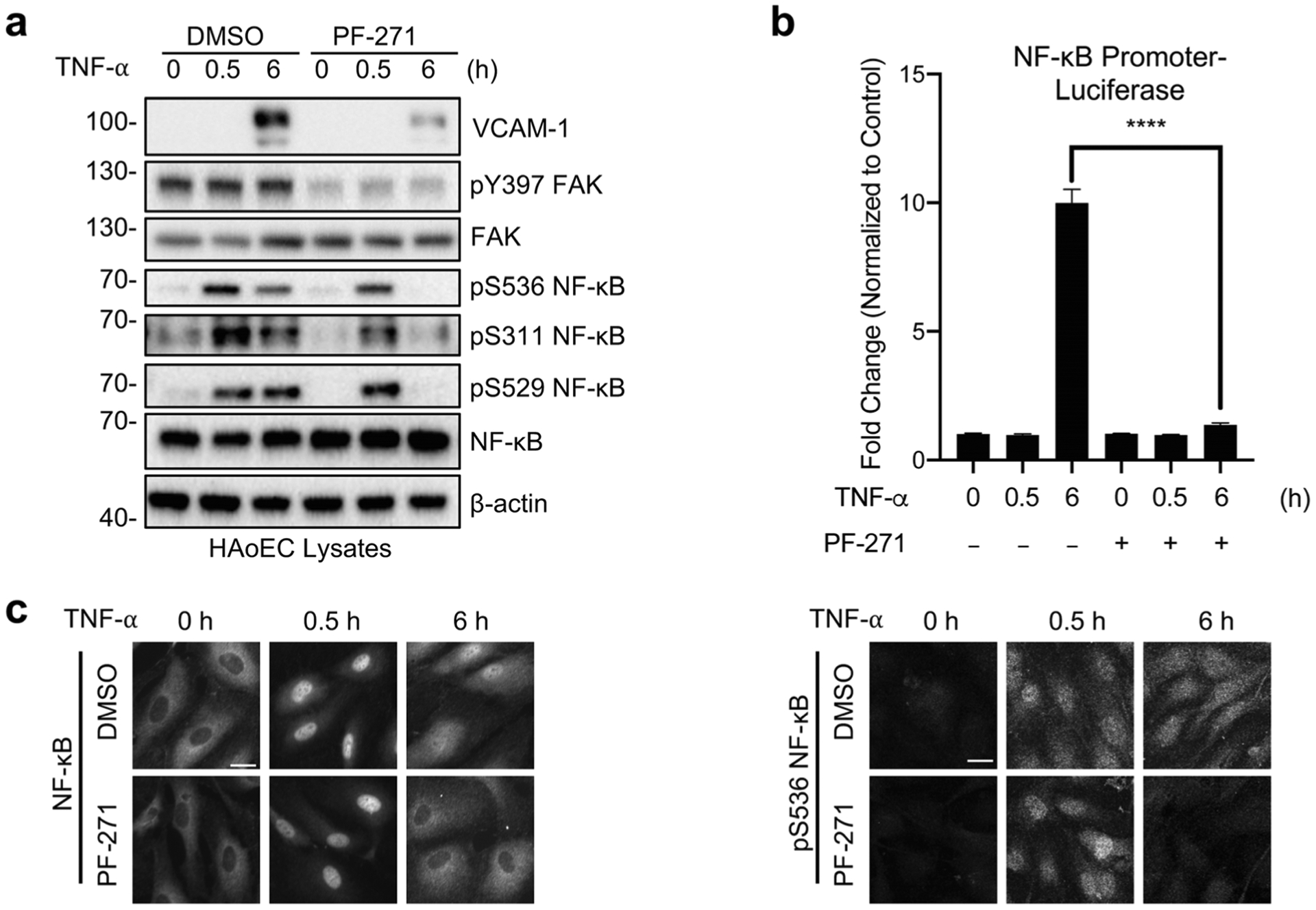
FAK inhibition decreases TNF-α-induced sustained NF-κB activation in endothelial cells. a–c HAoECs were treated for 1 h with DMSO or PF-271 (2.5 μmol/L) prior to TNF-α (10 ng/mL) stimulation for the indicated times. a Western blot analysis of VCAM-1, pY397 FAK, FAK, pS536 NF-κB, pS311 NF-κB, pS529 NF-κB, NF-κB, and β-actin (n = 3). b HAoECs were transfected with NF-κB promoter luciferase construct. Results are expressed as fold change over unstimulated control (n = 3). c Localization of NF-κB (rabbit) and expression of pS536 NF-κB (rabbit) were evaluated by immunostaining (n = 3). Scale bar, 20 μm. ****P < 0.0001.
