Fig. 5.
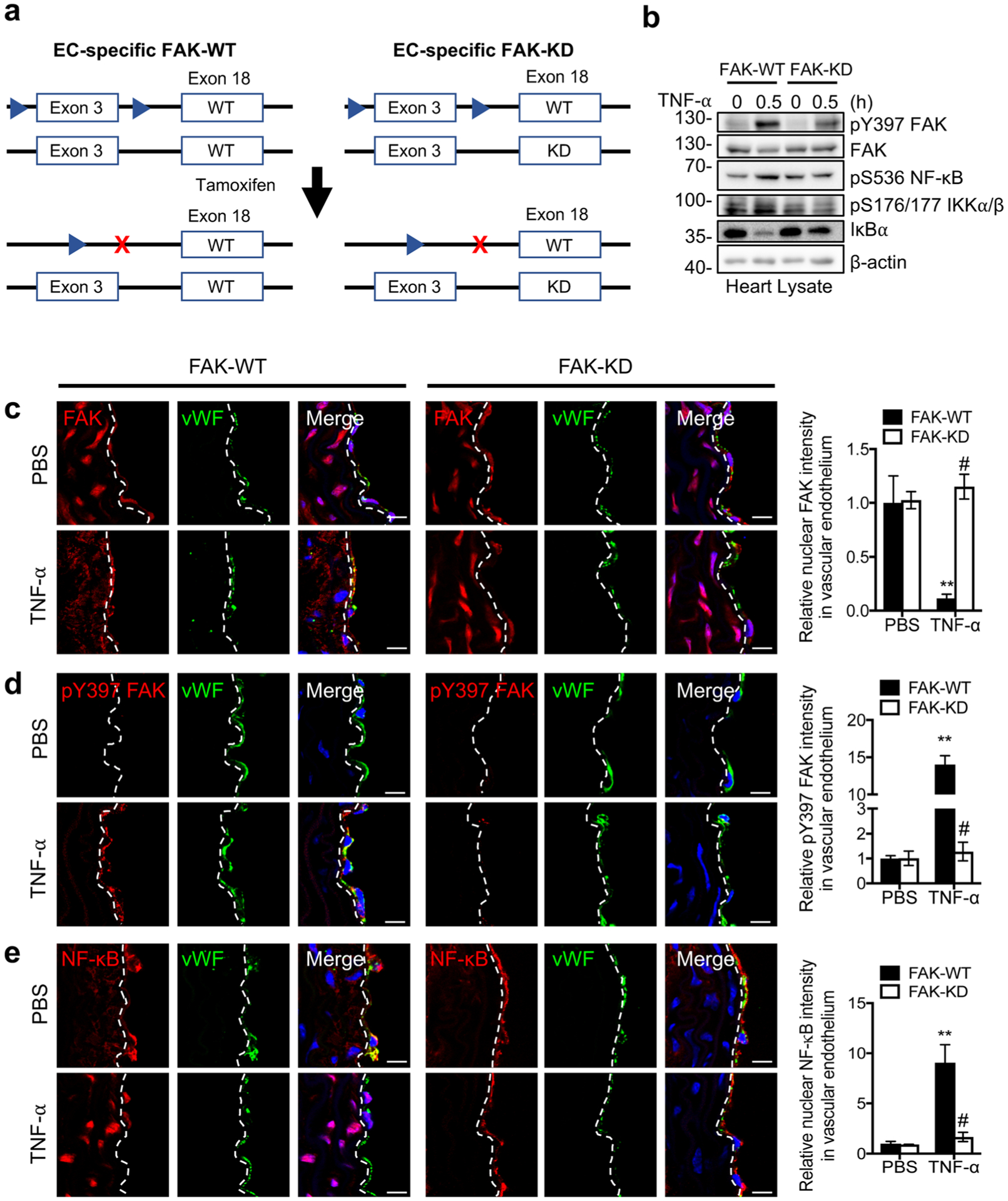
Immunostaining of mouse aortas showing that EC-specific FAK inhibition decreases TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in mice. a Schematic of the deletion of the FAK flox allele and generation of EC-specific FAK-WT and FAK-KD mice. EC-specific FAK-WT and FAK-KD mice were injected with PBS or mouse TNF-α (0.02 mg/kg) for 0.5 h. b Western blot analysis of heart lysates for pY397 FAK, FAK, pS536 NF-κB, pS176/177 IKKα/β, IκBα, and β-actin as loading control (n=4). Aortas sections were stained for FAK (red; mouse) (c), pY397 FAK (red; rabbit) (d), or NF-κB (red; rabbit) (e). ECs were stained with vWF (green; rabbit or mouse) and nuclei with DAPI (blue). Relative fluorescence intensity in vWF-positive ECs was reported as mean ± SD (n = 4). Dashed lines, boundary between media and EC on the basis of vWF staining. Scale bars, 10 μm. **P < 0.01 vs FAK-WT PBS; #P < 0.01 vs FAK-WT TNF-α.
